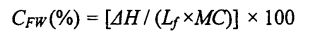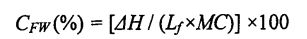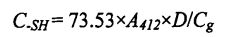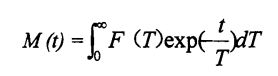Мұздатылған қамырдың өңдеу қасиеттерін жақсарту жоғары сапалы ыңғайлы бумен пісірілген нанның ауқымды өндірісін жүзеге асырудың белгілі бір практикалық маңызы бар. In this study, a new type of hydrophilic colloid (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, Yang, MC) was applied to frozen dough. The effects of 0.5%, 1%, 2%) on the processing properties of frozen dough and the quality of steamed bread were evaluated to evaluate the improvement effect of HPMC. Influence on the structure and properties of components (wheat gluten, wheat starch and yeast).
Түйінді сөздер: буланған нан; frozen dough; hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; бидай глютені; wheat starch; yeast.
Мазмұны
1-тарау Алғы сөздер ........................................................................................................................
1.1 Үйдегі және шетелдегі зерттеулердің қазіргі жағдайы .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1.1.4 Мұздатылған қамырдың проблемалары мен міндеттері ...............................................................................................
1.1.7 Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, I-IPMC) ………. 5
112 Зерттеудің мақсаты мен маңызы ...........................................................................
1.3 Зерттеудің негізгі мазмұны .......................................................................................................
2.2 Тәжірибелік материалдар мен әдістер .......................................................................
2.2.1 Тәжірибелік материалдар .................................................................................................................................................................
2.2.3 Тәжірибелік әдістер .............................................................................................................................................................................
2.3 Experimental results and discussion…………………………………………………………………… . 11
2.3.5 HPMC қосымшасының әсері және мұздатылған судың (GW) мұздатылған судың әсері (GW) мұздатылған қамырдағы (GW) .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
2.4 ТАРАУ ЖАҢАЛЫҚТАРЫ ........................................................................ 21
3.2.1 Тәжірибелік материалдар .........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3.2.2 Тәжірибелік аппараттар ...................................................................................
3.2.4 Experimental methods ....................................................................................................... 25
3.3.2 The effect of adding amount of HPMC and freezing storage time on the freezable moisture content (CFW) and thermal stability……………………………………………………………………. 30
3.3.3 HPMC қосымшасының әсері және сульфхидерл Мазмұны (C кеме) ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ . 34
4.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................................. . 44
4.2 Experimental materials and methods ................................................................................. 45
4.2.1 Тәжірибелік материалдар .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... .45
4.3 Analysis and discussion ........................................................................................................... 48
4.3.1 Content of basic components of wheat starch ……………………………………………………. 48
4.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the shear viscosity of starch paste………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 52
4.3.5 HPMC қосымшасының және мұздатылған сақтау уақытының крахмал ісіну қабілетіне әсері .............................................................................................................................................................
4.3.6 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and frozen storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 57
4.3.7 HPMC қосымшасының әсері және оны тоқтату уақытының әсері крахмалдың салыстырмалы кристалдылығында .............................................................................................................................
4.4 Chapter Summary ...................................................................................................................... 6 1
Chapter 5 Effects of HPMC addition on yeast survival rate and fermentation activity under frozen storage conditions………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 62
5.1Серілділік ................................................................................................................................................ 62
5.2 Материалдар мен әдістер ...................................................................... 62
5.2.1 Тәжірибелік материалдар мен құралдар ...........................................................................................
5.2.2 тәжірибелік әдістер. . . . . …………………………………………………………………………. 63
5.3 Results and Discussion ............................................................................................................... 64
5.3.1 HPMC қосымшасының және мұздату уақытының қамырдың емделетін биіктігіне әсері .............................................................................................................................................
5.3.3 Қамырдағы глутатионның мөлшері мен мұздату уақытының мөлшерін қосудың әсері ........................................................................................................................... «
5.4 Chapter Summary ........................................................................................................................ 67
6-тарау Қорытынды және перспективалар ...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
6.1 Қорытынды ................................................................ 68
6.2. 68
Суреттер тізімі
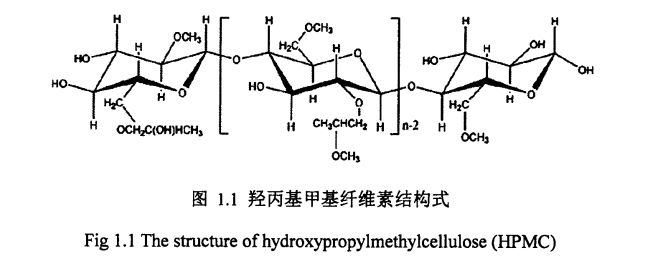
Figure 1.1 The structural formula of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose………………………. . 6
2.1-сурет HPMC қосымшасының мұздатылған қамырдың реологиялық қасиеттеріне әсері .........................................................................................................................................................
2.2-сурет. Бумен пісірілген нанның нақты көлеміне HPMC қосу және мұздату уақытының әсері .....................................................................................................................................................
2.3-сурет. HPMC қосымшасының және аязды уақытының бумен пісірілген нанның қаттылық әсері .........................................................................................................................................................................
2.4-сурет. HPMC қосымшасының және мұздату уақытының бумен пісірілген нанның серпімділігіне әсері ....................................................................................................................................... . 20
Figure 3.1 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the rheological properties of wet gluten…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 30
3.2-сурет Бидай глютенінің термодинамикалық қасиеттеріне HPMC қосу және мұздату уақытының әсері ........................................................................................................... . 34
Figure 3.3 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing time on free sulfhydryl content of wheat gluten……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 35
3.6 сурет ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 3.7 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the microscopic gluten network structure…………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 43
Сурет 4.1 Крахмалдан жасалған гелатинизацияға тән қисық ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 51
Figure 4.2 Fluid thixotropy of starch paste ................................................................................. 52
Figure 4.3 Effects of adding amount of MC and freezing time on the viscoelasticity of starch paste……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 57
Figure 4.5 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 59
Сурет 4.6 HPMC қосу және тоқтату Уақытының эффектілері крахмалдың XRD қасиеттеріне .........................................................................................................................................................
5.2-сурет. HPMC қосу және мұздату уақытының ашытқы өмір сүру деңгейіне әсері ......................................................................................................................................... 67
53-сурет Ашытқы (микроскопиялық сараптама) микроскопиялық бақылау ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 68
Table 2.1 The basic ingredient content of wheat flour…………………………………………………. 11
Кесте 3.1 Глютендегі негізгі ингредиенттердің мазмұны ...........................................................................................
Table 3.2 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the phase transition enthalpy (Yi IV) and freezer water content (e chat) of wet gluten………………………. 33
Table 3.3 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the peak temperature (product) of thermal denaturation of wheat gluten…………………………………………. 33
3.5 Кесте 3.5 HPMC қосу және мұздату уақыты бидай глютенінің екінші құрылымына әсер етеді .....................................................................................................................................................................
Table 3.6 Effects of I-IPMC addition and freezing storage time on the surface hydrophobicity of wheat gluten……………………………………………………………………………………………. 41
Кесте 4.1 Бидай крахмалының негізгі компоненттерінің мазмұны .....................................................................................................
Table 4.3 Effects of I-IPMC addition and freezing time on the shear viscosity of wheat starch paste…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 55
Кесте 4.4 Кестеде I-IPMC қосымшасының қосымшасы және мұздатылған сақтау уақыты крахмалды желатуизацияның термодинамикалық қасиеттеріне .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1.1.1 Бумен пісірілген нан
Қазіргі уақытта бумен пісірілген нан бойынша зерттеулер негізінен келесі аспектілерге бағытталған:
2)Research on the processing and compounding of special flour for steamed bread. The effect of flour properties on the quality of dough and steamed buns and the research on new special flour for steamed buns, and based on this, an evaluation model of flour processing suitability was established [7]; Мысалы, ұн мен бумен пісірілген бөрткіштердің сапасына түрлі ұн тарту әдістерінің әсері [7] 81; The effect of the compounding of several waxy wheat flours on the quality of steamed bread [9J et al.; Жу, Хуанг, Хан (2001) бидай ақуызының қамыр мен солтүстік бумен пісірілген нанның сапасына әсерін бағалады және Глиад / Глутенин қамырдың қасиеттерімен және бумен пісірілген нанмен салыстырғанда айтарлықтай кері әсер етті деп санады; Zhang, et a1. (2007) analyzed the correlation between gluten protein content, protein type, dough properties and steamed bread quality, and concluded that the content of high molecular weight glutenin subunit (1ligh.molecular-weight, HMW) and total protein content are all related to the quality of northern steamed bread. have a significant impact [11].
3) қамырды дайындау және бумен пісірілген нан дайындау технологиясы бойынша зерттеулер. Бумен пісірілген нан өндірісінің технологиялық жағдайының оның сапасына және процесті оңтайландыруға әсері бойынша зерттеулер; Liu changhonet және al. (2009) showed that in the process of dough conditioning, process parameters such as water addition, dough mixing time, and dough pH value have an impact on the whiteness value of steamed bread. Бұл сенсорлық бағалауға айтарлықтай әсер етеді. If the process conditions are not suitable, it will cause the product to turn blue, dark or yellow. The research results show that during the dough preparation process, the amount of water added reaches 45%, and the dough mixing time is 5 minutes, ~ When the pH value of the dough was 6.5 for 10 min, the whiteness value and sensory evaluation of the steamed buns measured by the whiteness meter were the best. Қамырды бір уақытта 15-20 рет жылжытқан кезде, қамыр - бұл қабыршақты, тегіс, серпімді және жылтыр бет; when the rolling ratio is 3:1, the dough sheet is shiny, and the whiteness of the steamed bread increases [l to; LI, және et. (2015) құрама ашытылған қамырдың өндірістік процесі және оны бумен пісірілген нан өңдеуге қолдану [13].
4) бумен пісірілген нанның сапасын жақсарту бойынша зерттеулер. Бумен пісірілген нан сапасының импроваторларын қосу және қолдану бойынша зерттеулер; mainly including additives (such as enzymes, emulsifiers, antioxidants, etc.) and other exogenous proteins [14], starch and modified starch [15], etc. The addition and optimization of the corresponding process It is particularly noteworthy that in recent years, through the use of some exogenous proteins and other additives, gluten-free (free. gluten) pasta products have been developed to meet the requirements of celiac disease (Dietary needs of patients with Coeliac Disease [16.1 cit.
5) бумен пісірілген нан мен тиісті тетіктерді сақтау және қартаю. Pan lijun et al. (2010) optimized the composite modifier with good anti-aging effect through experimental design [l do not; Wang, et a1. (2015) studied the effects of gluten protein polymerization degree, moisture, and starch recrystallization on the increase of steamed bread hardness by analyzing the physical and chemical properties of steamed bread. Нәтижелерде судың жоғалуы мен крахмал қайта репризистизациясы бумен пісірілген нанның қартаюының негізгі себептері болды (20].
6)Research on the application of new fermented bacteria and sourdough. Jiang, et a1. (2010) Application of Chaetomium sp. fermented to produce xylanase (with thermostable) in steamed bread [2l'; Gerez, et a1. (2012) ашытылған ұн өнімдеріндегі сүт қышқылы бактерияларының екі түрін пайдаланып, олардың сапасын бағалады [221; Wu, et al. (2012) studied the influence of sourdough fermented by four kinds of lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus, sanfranciscemis , Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp bulgaricus) on the quality (specific volume, texture, fermentation flavor, etc.) of northern steamed bread [23]; және Герес және А1. (2012) used the fermentation characteristics of two kinds of lactic acid bacteria to accelerate the hydrolysis of gliadin to reduce the allergenicity of flour products [24] and other aspects.
Олардың ішінде бумен пісірілген нан кәдімгі сақтау шарттары бойынша қартаюға бейім, бұл бумен пісірілген нан өндірісі мен өңдеуді өңдеуді шектейтін маңызды фактор болып табылады. After aging, the quality of steamed bread is reduced - the texture becomes dry and hard, dregs, shrinks and cracks, the sensory quality and flavor deteriorate, the digestion and absorption rate decreases, and the nutritional value decreases. This not only affects its shelf life, but also creates a lot of waste. According to statistics, the annual loss due to aging is 3% of the output of flour products. 7%. With the improvement of people's living standards and health awareness, as well as the rapid development of the food industry, how to industrialize the traditional popular staple noodle products including steamed bread, and obtain products with high quality, long shelf life and easy preservation to meet the needs of the growing demand for fresh, safe, high-quality and convenient food is a long-standing technical problem. Based on this background, frozen dough came into being, and its development is still in the ascendant.
1.1.3 Мұздатылған қамырға дейін
Мұздатылған қамыр 1950 жылдары жасалған ұн өнімдерін өңдеу және өндірудің жаңа технологиясы болып табылады. It mainly refers to the use of wheat flour as the main raw material and water or sugar as the main auxiliary materials. Baked, packed or unpacked, quick-freezing and other processes make the product reach a frozen state, and in. For products frozen at 18"C, the final product needs to be thawed, proofed, cooked, etc. [251].
Өндіріске сәйкес, мұздатылған қамырды шамамен төрт түрге бөлуге болады.
в) алдын-ала өңделген қамыр: Қамыр бір бөлікке бөлінеді және құрылады, содан кейін дайындалған (белгілі бір дәрежеде), салқындатылған, мұздатылған, мұздатылған, сақталған, ерітілген және пісірілген (пісіру, бумен пісіру және т.б.)
The emergence of frozen dough not only creates conditions for the industrialization, standardization, and chain production of fermented pasta products, it can effectively shorten processing time, improve production efficiency, and reduce production time and labor costs. Therefore, the aging phenomenon of the pasta food is effectively inhibited, and the effect of prolonging the shelf life of the product is achieved. Сондықтан, әсіресе Еуропада, Америкада, Америкада, Жапонияда және басқа елдерде, мұздатылған қамыр, француз тәтті нан (француздық тәтті нан), кішкентай мафин (муфт), нан орамдары (орамдар), француз багет (- таяқша), печенье және мұздатылған
Cakes and other pasta products have different degrees of application [26-27]. Толық емес статистикаға сәйкес, 1990 жылға қарай АҚШ-тағы наубайханалардың 80% -ы мұздатылған қамырды қолданған; Жапониядағы наубайханалардың 50% -ы мұздатылған қамырды да қолданды. ХХ ғасыр
1.1.4 Мұздатылған қамырдың шақырушылары мен қиындықтары
Қамыр - көп компонент (ылғал, ақуыз, крахмал, микроорганизм және т.б.), көп фазалы (сұйық, сұйық интерфейс), көп фазалы (макромолекулалар), көп мөлшерде (сұйық интерфейс), қатты сұйық интерфейс) 1281, сондықтан жоғарыда аталған сапаның нашарлауының себептері өте күрделі және алуан түрлі.
Көптеген зерттеулер мұздатылған тағамдардағы мұз кристалдарының пайда болуы мен өсуі өнімнің сапасының нашарлауына әкелетін маңызды фактор екенін анықтады [291]. Ice crystals not only reduce the survival rate of yeast, but also weaken the gluten strength, affect the starch crystallinity and gel structure, and damage the yeast cells and release the reducing glutathione, which further reduces the gas holding capacity of gluten. In addition, in the case of frozen storage, temperature fluctuations can cause ice crystals to grow due to recrystallization [30]. Therefore, how to control the adverse effects of ice crystal formation and growth on starch, gluten and yeast is the key to solving the above problems, and it is also a hot research field and direction. In the past ten years, many researchers have been engaged in this work and achieved some fruitful research results. However, there are still some gaps and some unresolved and controversial issues in this field, which need to be further explored, such as:
а) Мұздатылған қамырдың сапасының нашарлауын қалай тоқтату керек, әсіресе, мұздатылған сақтау уақытының ұзартылуымен, әсіресе қамырдың (крахмал, глютен және ашытқы) құрылымы мен қасиеттеріне қалай әсер етуі керек. Hotspots and fundamental issues in this research field;
c)Expand, optimize and use new frozen dough quality improvers, which is conducive to the optimization of production enterprises and the innovation and cost control of product types. Қазіргі уақытта ол әлі де одан әрі нығайтып, кеңейту керек;
1.1.5 Мұздатылған қамырдың ғылыми-зерттеу деңгейі
i.Study the changes in the structure and properties of frozen dough with the extension of freezing storage time, in order to explore the reasons for the deterioration of product quality, especially the effect of ice crystallization on biological macromolecules (protein, starch, etc.), for example, ice crystallization. Formation and growth and its relationship with water state and distribution; changes in wheat gluten protein structure, conformation and properties [31]; changes in starch structure and properties; Қамырды микроқұрылым мен байланысты қасиеттердің өзгеруі және т.б. 361.
Ii. Optimization of frozen dough production process, frozen storage conditions and formula. During the production of frozen dough, temperature control, proofing conditions, pre-freezing treatment, freezing rate, freezing conditions, moisture content, gluten protein content, and thawing methods will all affect the processing properties of frozen dough [37]. In general, higher freezing rates produce ice crystals that are smaller in size and more uniformly distributed, while lower freezing rates produce larger ice crystals that are not uniformly distributed. In addition, a lower freezing temperature even below the glass transition temperature (CTA) can effectively maintain its quality, but the cost is higher, and the actual production and cold chain transportation temperatures are usually small. In addition, the fluctuation of the freezing temperature will cause recrystallization, which will affect the quality of the dough.
Iii. Using additives to improve the product quality of frozen dough. In order to improve the product quality of frozen dough, many researchers have made explorations from different perspectives, for example, improving the low temperature tolerance of material components in frozen dough, using additives to maintain the stability of the dough network structure [45.56], etc. Among them, the use of additives is an effective and widely used method. Негізінен, i) ферменттік препараттар, мысалы, трансглютаминаза, O [. Амилаза; ii) эмульгаторлар, мысалы, моноглицеридтер стеараты, мәліметтер, SSL, CSL, мәліметтер және т.б. сияқты эмульгаторлар; iii) антиоксиданттар, аскорбин қышқылы және т.б.; iv) polysaccharide hydrocolloids, such as guar gum, yellow Originalgum, gum Arabic, konjac gum, sodium alginate, etc.; v) XU және A1 сияқты басқа функционалды заттар. (2009) added Ice-structuring Proteins to wet gluten mass under freezing conditions, and studied its protective effect and mechanism on the structure and function of gluten protein [y71.
Ⅳ. Breeding of antifreeze yeast and application of new yeast antifreeze [58-59]. Сасано және А1. (2013) obtained freeze-tolerant yeast strains through hybridization and recombination between different strains [60-61], and S11i, Yu, & Lee (2013) studied a biogenic ice nucleating agent derived from Erwinia Herbicans used to protect the fermentation viability of yeast under freezing conditions [62J.
The chemical nature of hydrocolloid is a polysaccharide, which is composed of monosaccharides (glucose, rhamnose, arabinose, mannose, etc.) through 0 [. 1-4. Glycosidic bond or/and a. 1--"6. Glycosidic bond or B. 1-4. Glycosidic bond and 0 [.1-3. The high molecular organic compound formed by the condensation of glycosidic bond has a rich variety and can be roughly divided into: ① Cellulose derivatives , such as methyl cellulose (MC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC); ② plant polysaccharides, such as konjac gum, guar gum, gum Arabic ; ③ seaweed polysaccharides, such as seaweed gum, carrageenan; ④ microbial polysaccharides, such as Xanthan gum .Polysaccharide has strong hydrophilicity because it contains a large number of hydroxyl groups that are easy to form hydrogen bonds with water, and has the functions of controlling the migration, state and distribution of water in the food system. Therefore, the addition of hydrophilic colloids gives food Many functions, properties, and qualities of hydrocolloids are closely related to the interaction between polysaccharides and water and other macromolecular substances. At the same time, due to the multiple functions of thickening, stabilizing, and water retention, hydrocolloids are widely used to include in the food processing of flour products. Wang xin және al. (2007) балдырлар полисахаридтер мен желатинді қамырдың әйнекті өтпелі температурасына қосудың әсерін зерттеді [631. Ванг Юшенг және басқалар. (2013) әр түрлі гидрофильді коллоидтардың қосылыстары қамырдың ағынын едәуір өзгертуі мүмкін деп санайды. Change the properties, improve the tensile strength of the dough, enhance the elasticity of the dough, but reduce the extensibility of the dough [delete.
1.11.7hydroxypropypl метил целлюлозасы (гидроксиппил метил целлюлозасы, i-IPMC)
Сызықтық молекулалық тізбектегі және кристалды құрылымдағы сутегі байланыстарының болуына байланысты целлюлоза судың ерігіштігін нашарлатады, бұл оның қолданылу ауқымын шектейді. However, the presence of substituents on the side chain of HPMC breaks the intramolecular hydrogen bonds, making it more hydrophilic [66l], which can quickly swell in water and form a stable thick colloidal dispersion at low temperatures Tie. Гидролюзиозды гидроциат негізіндегі гидрофильдік коллоид ретінде HPMC материалдар, паператор, тоқыма, косметика, фармацевтика және тамақ салаларында кеңінен қолданылған [6 71]. In particular, due to its unique reversible thermo-gelling properties, HPMC is often used as a capsule component for controlled release drugs; Азық-түлікке, HPMC сонымен қатар беттік-белсенді зат, қалыңдатқыштар, эмульгаторлар, тұрақтандырғыштар, тұрақтандырғыштар және т.б. ретінде қолданылады және тиісті өнімдердің сапасын жақсартуда және нақты функцияларды жүзеге асыруда рөл ойнайды. Мысалы, HPMC қосу крахмалдың желатинизация сипаттамаларын өзгерте алады және крахмал пастасының гель күштерін азайтады. , HPMC азық-түліктегі ылғалдың жоғалуын азайтып, нанның қаттылығын азайтып, нанның қартаюын тиімді тежеуі мүмкін.
Макаронда HPMC белгілі бір дәрежеде қолданылғанмен, ол негізінен қартаюға қарсы агент және нан үшін суды сақтайтын агент ретінде пайдаланылады, бұл өнімнің нақты көлемін, текстуралық қасиеттерін, текстуралық қасиеттерін және сақтау мерзімін ұзартады. However, compared with hydrophilic colloids such as guar gum, xanthan gum, and sodium alginate [75-771], there are not many studies on the application of HPMC in frozen dough, whether it can improve the quality of steamed bread processed from frozen dough. Оның әсері туралы әлі де тиісті есептер жоқ.
1.2Сіздің мәні және маңызы
At present, the application and large-scale production of frozen dough processing technology in my country as a whole is still in the development stage. Сонымен бірге, мұздатылған қамырдың өзінде белгілі бір қиындықтар мен кемшіліктер бар. These comprehensive factors undoubtedly restrict the further application and promotion of frozen dough. on the other hand,this also means that the application of frozen dough has great potential and broad prospects, especially from the perspective of combining frozen dough technology with the industrialized production of traditional Chinese noodles (non-)fermented staple food, to develop more products that meet the needs of Chinese residents. It is of practical significance to improve the quality of the frozen dough based on the characteristics of Chinese pastry and the dietary habits, and is suitable for the processing characteristics of Chinese pastry.
Мұздатылған қамырдың құрылымы мен қасиеттеріне, мұздатылған қамырдан жасалған бұйымдардың, мұздатылған қамырдан жасалған бұйымдардың (бумен пісірілген нан) әсері, бидай крахмалының құрылымы мен қасиеттері, бидай крахмалының құрылымы мен қасиеттері, және ашытқының құрылымы. Based on the above considerations, the following experimental design was made in this research topic:
1)Select a new type of hydrophilic colloid, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) as an additive, and study the addition amount of HPMC under different freezing time (0, 15, 30, 60 days; the same below) conditions. (0%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%; the same below) on the rheological properties and microstructure of frozen dough, as well as on the quality of the dough product - steamed bread (including the specific volume of steamed bread) , texture), investigate the effect of adding HPMC to the frozen dough on the processing properties of the dough and the quality of steamed bread, and evaluate the improvement effect of HPMC on the processing properties of the мұздатылған қамыр;
2) жетілдіру механизмінің тұрғысынан, сулы глютен массасының реологиялық қасиеттеріне әртүрлі HPMC толықтыруларының әсері, су күйінің ауысуы және бидай глютенінің құрылымы мен қасиеттері әртүрлі ұстау уақытының шарттары бойынша зерттелді.
2.1
2.2 Тәжірибелік материалдар мен әдістер
Zhongyu Wheat Flour Binzhou Zhongyu Food Co., Ltd.; Angel Dry Yeter yester yetsaster ymel yast yster, ltd; HPMC (метилді ауыстыру деңгейі 28% .30%, гидроксиппилді алмастыру 7% .12%) Аладдин (Шанхай) химиялық реагентті компания; Осы экспериментте қолданылатын барлық химиялық реагенттер аналитикалық сыныпқа жатады;
BPS. 500CL constant temperature and humidity box
TA-XT плюс физикалық меншік сынағышы
SM. 986с қамыр араластырғыш
C21. KT2134 индукциялық пеш
Ұнтақты өлшеуіш. Е е
Extensometer. Е е
Q200 Дифференциалды сканерлеу калориметрі
KJELTEE TM 8400 Автоматты kjeldahl азот анализаторы
Фабрикант
Shanghai Yiheng Service Cocial Co., Ltd.
Shanghai Yiheng Service Cocial Co., Ltd.
Guangdong Midea Life Production Co., Ltd.
American TA компаниясы
American TA компаниясы
Huang Shi Heng Feng Medical жабдықтары Co., Ltd.
2.2.3 Эксперименталды әдіс
2.2.3.1 Ұнның негізгі компоненттерін анықтау
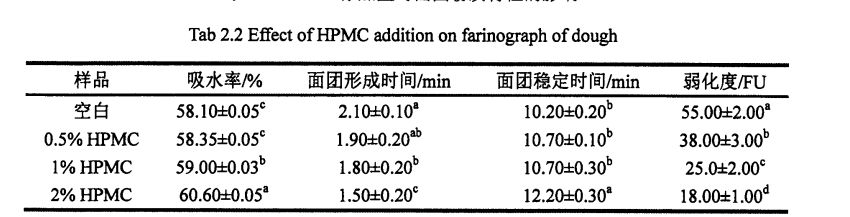
GB / T 14614.2006 анықтамалық әдісіне сәйкес, қамырдың фариндік қасиеттерін анықтау [821.
2.2.3.5 Қамырдың реологиялық қасиеттерін анықтау
A sample (about 2 g) of the central part of the partially melted dough was cut and placed on the bottom plate of the rheometer (Discovery R3). First, the sample was subjected to dynamic strain scanning. The specific experimental parameters were set as follows: A parallel plate with a diameter of 40 mm was used, the gap was set to 1000 mln, the temperature was 25 °C, and the scanning range was 0.01%. 100%, the sample rest time is 10 min, and the frequency is set to 1Hz. The Linear Viscoelasticity Region (LVR) of the tested samples was determined by strain scanning. Then, the sample was subjected to a dynamic frequency sweep, and the specific parameters were set as follows: the strain value was 0.5% (in the LVR range), the resting time, the fixture used, the spacing, and the temperature were all consistent with the strain sweep parameter settings. Five data points (plots) were recorded in the rheology curve for each 10-fold increase in frequency (linear mode). After each clamp depression, the excess sample was gently scraped with a blade, and a layer of paraffin oil was applied to the edge of the sample to prevent water loss during the experiment. Әр үлгі үш рет қайталанды.
Толығымен ерітілген қамырдың орталық бөлігінің үлгісін өлшеу, оны алюминийден жасалған (сұйық үлгілерге жарайды) және оны дифференциалды сканерлеу калориметрі (DSC) өлшеп, оны өлшеп алыңыз. The specific program parameters are set. Келесідей: алдымен 5 минут ішінде 20 ° C температурада, содан кейін 10 минут ішінде .30 ° C-қа дейін төмендейді, содан кейін 5 »с / минутта 25 ° C-қа дейін төмендейді, ал тазартылған газ азот (N2) және оның ағын-шашын мөлшері 50 мл / мин болды. Анықтама ретінде алынған бос алюминийді қолдана отырып, алынған DSC қисығы Anmannal Analysis 2000 талдау бағдарламалық жасақтамасының көмегімен талданды, ал мұз кристалының еріту энтальпиясы (күні) шыңы шамамен 0 ° C температурада алынды. Терең судың мөлшері (CFW) келесі формула бойынша есептеледі [85.86]:
Among them, 厶 represents the latent heat of moisture, and its value is 334 J Dan; MC (total Moisture Content) represents the total moisture content in the dough (measured according to GB 50093.2010t78]). Әр үлгі үш рет қайталанды.
Тиісті уақыт өткеннен кейін, мұздатылған қамыр 4 сағат ішінде 4 ° C тоңазытқышта 4 ° C тоңазытқышта түсірілген, содан кейін мұздатылған қамырды ерігенше бөлме температурасына қойды. Divide the dough into about 70 grams per portion, knead it into shape, and then put it into a constant temperature and humidity box, and proof it for 60 minutes at 30°C and a relative humidity of 85%. After proofing, steam for 20 min, and then cool for 1 h at room temperature to evaluate the quality of steamed bread.
Бумен пісірілген нанның нақты көлемі (CM3 / G) = Бумен пісірілген нан көлемі (CM3) / Бумен пісірілген нан массасы (G)
(2) бумен пісірілген нанның құрылымын анықтау
All experiments were repeated at least three times unless otherwise specified, and the experimental results were expressed as the mean (Mean) ± standard deviation (Standard Deviation). SPSS статистикасы 19 дисперсияны талдау үшін пайдаланылды (дисперсияны талдау), ал маңыздылық деңгейі o. 05; Тиісті диаграммаларды салу үшін 8.0 пайдаланыңыз.
2.3 Тәжірибелік нәтижелер және талқылау
2.3.1 Бидай ұнының негізгі құрамдас индексі
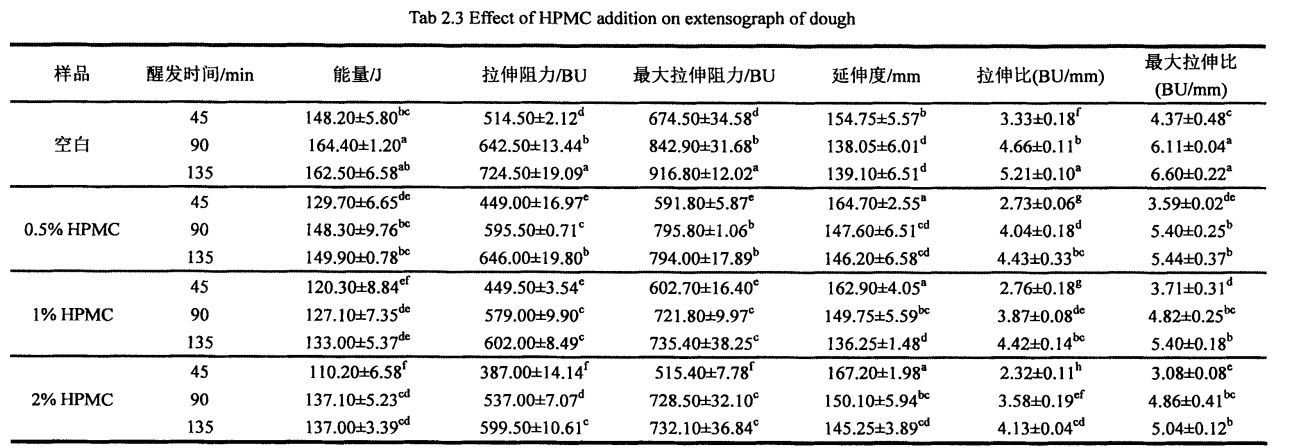
The tensile properties of the dough can better reflect the processing properties of the dough after proofing, including the extensibility, tensile resistance and stretch ratio of the dough. The tensile properties of the dough are attributed to the extension of the glutenin molecules in the dough extensibility, as the cross-linking of glutenin molecular chains determines the elasticity of the dough [921]. Termonia, Smith (1987) [93] believed that the elongation of polymers depends on two chemical kinetic processes, that is, the breaking of secondary bonds between molecular chains and the deformation of cross-linked molecular chains. Молекулалық тізбектердің деформациялану деңгейі салыстырмалы түрде төмен болған кезде, молекулалық тізбек жеткілікті және тез молекулалық тізбекті созу арқылы пайда бола алмайды, бұл өз кезегінде молекулалық тізбектердің сынуына әкеледі, сонымен қатар молекулалық тізбектердің ұзындығы да қысқа. Молекулалық тізбектердің деформациялану деңгейі тек молекулалық тізбекті тез және жеткілікті түрде де, жеткілікті болуы мүмкін, ал молекулалық тізбектегі коваленттік облигациялар түйіндері бұзылмайды, ал полимердің ұзартылуын арттыруға болады. Сондықтан, глютен протеин желісінің деформациясы мен созылу әрекетін өзгерту қамырдың созылу қасиеттеріне әсер етеді [92].
Table 2.3 lists the effects of different amounts of HPMC (O, 0.5%, 1% and 2%) and different proofing 1'9 (45 min, 90 min and 135 min) on the dough tensile properties (energy, stretch resistance, maximum stretch resistance, elongation, stretch ratio and maximum stretch ratio). The experimental results show that the tensile properties of all dough samples increase with the extension of the proofing time except the elongation which decreases with the extension of the proofing time. For the energy value, from 0 to 90 min, the energy value of the rest of the dough samples increased gradually except for the addition of 1% HPMC, and the energy value of all dough samples increased gradually. Ешқандай өзгерістер болған жоқ. This shows that when the proofing time is 90 min, the network structure of the dough (cross-linking between molecular chains) is completely formed. Therefore, the proofing time is further extended, and there is no significant difference in the energy value. At the same time, this can also provide a reference for determining the proofing time of the dough. As the proofing time prolongs, more secondary bonds between molecular chains are formed and the molecular chains are more closely cross-linked, so the tensile resistance and the maximum tensile resistance increase gradually. Сонымен бірге, молекулалық тізбектердің деформация деңгейі молекулалық тізбектер арасындағы қайталама облигациялардың өсуімен және молекулалық тізбектердің қатаюымен байланысты, олар қамырдың ұзартылуының төмендеуіне әкеліп соқтырады, бұл қамырдың ұзартылуына әкелді. The increase in tensile resistance/maximum tensile resistance and the decrease in elongation resulted in an increase in tensile LL/maximum tensile ratio.
Алайда, HPMC қосу жоғарыда аталған трендті тиімді түрде баса алады және қамырдың созылу қасиеттерін өзгертеді. With the increase of HPMC addition, the tensile resistance, maximum tensile resistance and energy value of the dough all decreased correspondingly, while the elongation increased. Specifically, when the proofing time was 45 min, with the increase of HPMC addition, the dough energy value decreased significantly, from 148.20-J: 5.80 J (blank) to 129.70-J respectively: 6.65 J (add 0.5% HPMC), 120.30 ± 8.84 J (add 1% HPMC), and 110.20-a: 6.58
J (2% HPMC added). At the same time, the maximum tensile resistance of the dough decreased from 674.50-a: 34.58 BU (blank) to 591.80--a: 5.87 BU (adding 0.5% HPMC), 602.70± 16.40 BU (1% HPMC added), and 515.40-a: 7.78 BU (2% HPMC added). However, the elongation of the dough increased from 154.75+7.57 MITI (blank) to 164.70-a: 2.55 m/rl(adding 0.5% HPMC), 162.90-a: 4 .05 min (1% HPMC added), and 1 67.20-a: 1.98 min (2% HPMC added). Бұл пластмасивтер суларының мөлшерін жоғарылату арқылы, ол грцен протеинінің молекулалық тізбегінің деформациясына қарсы немесе HPMC және глютенді протеиннің молекулалық тізбегінің өзара әрекеттесуіне байланысты болуы мүмкін, бұл оның созылу әрекетін өзгертеді, бұл өз кезегінде ол қамырдың тиімділігі қасиеттерін жақсартады және сапаға әсер етеді, бұл сапаға әсер етеді (мысалы, нақты көлем) texture) of the final product.
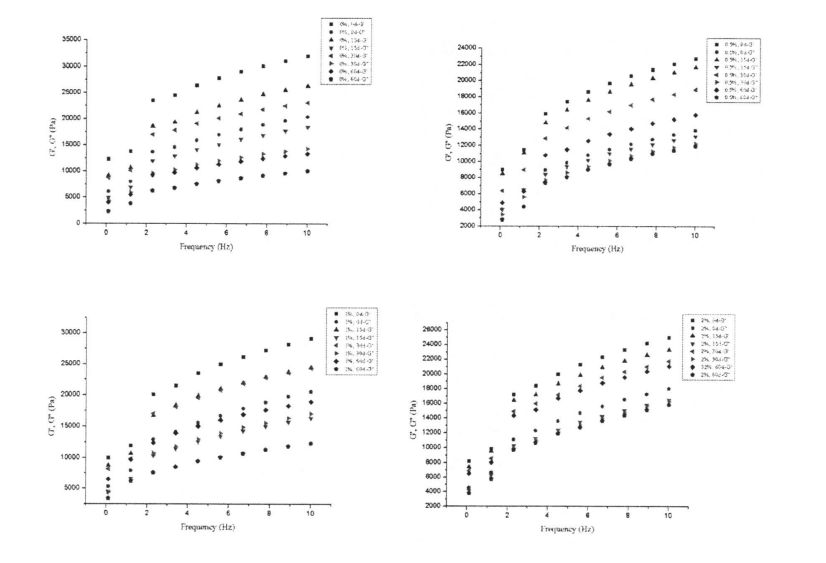
Figure 2.1 shows the change of storage modulus (elastic modulus, G') and loss modulus (viscous modulus, G") of dough with different HPMC content from 0 days to 60 days. The results showed that with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the G' of the dough without adding HPMC decreased significantly, while the change of G" was relatively small, and the /an Q (G''/G') increased. This may be due to the fact that the network structure of the dough is damaged by ice crystals during freezing storage, which reduces its structural strength and thus the elastic modulus decreases significantly. Алайда, HPMC қосымшасының жоғарылауымен g-тің өзгеруі біртіндеп төмендеді. In particular, when the added amount of HPMC was 2%, the variation of G' was the smallest. Бұл HPMC мұз кристалдарының түзілуіне және мұз кристалдарының мөлшерінің өсуіне әсер ете алатындығын көрсетеді, осылайша қамырдың құрылымына зиян келтіреді және қамырдың құрылымдық беріктігін азайтады. In addition, the G' value of dough is greater than that of wet gluten dough, while the G" value of dough is smaller than that of wet gluten dough, mainly because the dough contains a large amount of starch, which can be adsorbed and dispersed on the gluten network structure. It increases its strength while retaining excess moisture.
2.3.5 HPMC қосымшасының әсері және мұздатылған қамырдағы судың мөлшері (қосылған)
2.3.6.1 HPMC қосымшасының мөлшері мен мұздатылған сақтау уақытының буға пісірілген нанның нақты көлеміне әсері
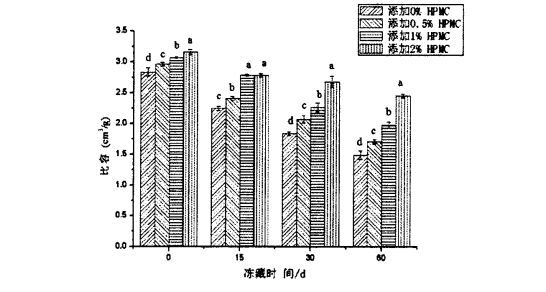
Бумен пісірілген нанның нақты көлемі бумен пісірілген нанның сыртқы келбеті мен сенсорлық сапасын жақсырақ көрсетеді. The larger the specific volume of the steamed bread, the larger the volume of the steamed bread of the same quality, and the specific volume has a certain influence on the appearance, color, texture, and sensory evaluation of the food. Әдетте, үлкенірек, бумен пісірілген тоқаштар белгілі бір дәрежеде тұтынушылармен танымал.
2-сурет, HPMC қосу және мұздатылған қойманың қытай буланған нанының нақты көлеміне әсері
Бумен пісірілген нанның нақты көлемі бумен пісірілген нанның сыртқы келбеті мен сенсорлық сапасын жақсырақ көрсетеді. The larger the specific volume of the steamed bread, the larger the volume of the steamed bread of the same quality, and the specific volume has a certain influence on the appearance, color, texture, and sensory evaluation of the food. Әдетте, үлкенірек, бумен пісірілген тоқаштар белгілі бір дәрежеде тұтынушылармен танымал.
However, the specific volume of the steamed bread made from frozen dough decreased with the extension of the frozen storage time. Among them, the specific volume of the steamed bread made from the frozen dough without adding HPMC was 2.835±0.064 cm3/g (frozen storage). 0 days) down to 1.495±0.070 cm3/g (frozen storage for 60 days); while the specific volume of steamed bread made from frozen dough added with 2% HPMC dropped from 3.160±0.041 cm3/g to 2.160±0.041 cm3/g. 451±0.033 cm3/g, therefore, the specific volume of the steamed bread made from the frozen dough added with HPMC decreased with the increase of the added amount. Since the specific volume of steamed bread is not only affected by the yeast fermentation activity (fermentation gas production), the moderate gas holding capacity of the dough network structure also has an important impact on the specific volume of the final product [96'9 cited. The measurement results of the above rheological properties show that the integrity and structural strength of the dough network structure are destroyed during the freezing storage process, and the degree of damage is intensified with the extension of the freezing storage time. Процесс барысында оның газ ұстау қабілеті нашар, бұл өз кезегінде бумен пісірілген нанның нақты көлемінің төмендеуіне әкеледі. However, the addition of HPMC can more effectively protect the integrity of the dough network structure, so that the air-holding properties of the dough are better maintained, therefore, in O. During the 60-day frozen storage period, with the increase of HPMC addition, the specific volume of the corresponding steamed bread decreased gradually.
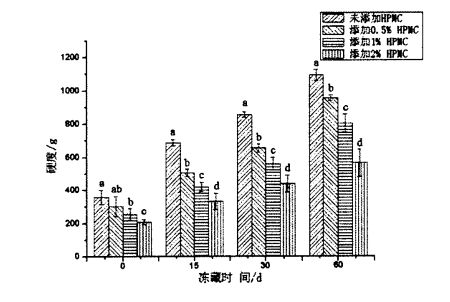
TPA (Tuptral Profile талдауы) Физикалық меншік сынағы макарон тағамдарының механикалық қасиеттері мен сапасын, оның ішінде қаттылық, серпімділік, біртұтас, икемділік пен икемділіктерін жан-жақты көрсетеді. Figure 2.3 shows the effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the hardness of steamed bread. The results show that for fresh dough without freezing treatment, with the increase of HPMC addition, the hardness of steamed bread significantly increases. decreased from 355.55±24.65g (blank sample) to 310.48±20.09 g (add O.5% HPMC), 258.06±20.99 g (add 1% t-IPMC) and 215.29 + 13.37 g (2% HPMC added). This may be related to the increase in specific volume of steamed bread. In addition, as can be seen from Figure 2.4, as the amount of HPMC added increases, the springiness of steamed bread made from fresh dough increases significantly, from 0.968 ± 0.006 (blank) to 1, respectively. .020 ± 0.004 (add 0.5% HPMC), 1.073 ± 0.006 (add 1% I-IPMC) and 1.176 ± 0.003 (add 2% HPMC). The changes of the hardness and elasticity of steamed bread indicated that the addition of HPMC could improve the quality of steamed bread. Бұл Розелл, Рожастың, Рожастың, Бенедито де Барбердің зерттеу нәтижелеріне сәйкес келеді [95] және Баркенас (95), Розелс (2005), яғни HPMC нанның қаттылығын едәуір азайтып, нан сапасын едәуір азайтады.
Екінші жағынан, мұздатылған қамырдың мұздатылған уақытын ұзартылған кезде, бумен пісірілген нанның қаттылығы оның қаттылығы едәуір артты (P <0.05), ал серпімділік едәуір төмендеді (P <0.05). Алайда, үрленген қамырдан алынған буға пісірілген қақпақтардан алынған, қосымша HPMC қаттылығы 358,267 ± 42,103 г дейін (мұздатылған қойма) 1092.014-тен 1092.014 ± 34.254 г дейін (мұздатылған қойма) (60 күн ішінде);
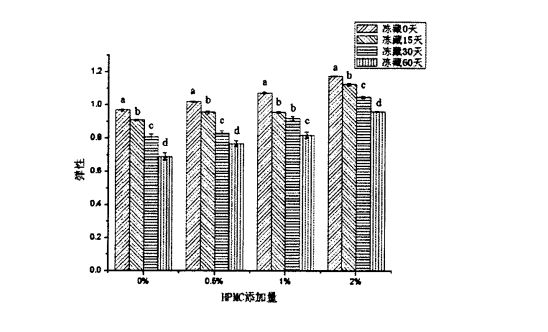
The hardness of the steamed bread made of frozen dough with 2% HPMC increased from 208.233 ± 15.566 g (frozen storage for 0 days) to 564.978 ± 82.849 g (frozen storage for 60 days). Fig 2.4 Effect of HPMC addition and frozen storage on springiness of Chinese steamed bread In terms of elasticity, the elasticity of steamed bread made from frozen dough without adding HPMC decreased from 0.968 ± 0.006 (freezing for 0 days) to 0.689 ± 0.022 (frozen for 60 days); Frozen with 2% HPMC added the elasticity of the steamed buns made of dough decreased from 1.176 ± 0.003 (freezing for 0 days) to 0.962 ± 0.003 (freezing for 60 days). Obviously, the increase rate of hardness and the decrease rate of elasticity decreased with the increase of the added amount of HPMC in the frozen dough during the frozen storage period. This shows that the addition of HPMC can effectively improve the quality of steamed bread. In addition, Table 2.5 lists the effects of HPMC addition and frozen storage time on other texture indexes of steamed bread. ) had no significant change (P>0.05); Алайда, 0 күнде мұздату кезінде, HPMC қосымшасының жоғарылауымен, гумизм мен реңк едәуір төмендеді (б
Екінші жағынан, мұздату уақытын ұзартумен, бумен пісірілген нанның бірігу және қалпына келтіру күші айтарлықтай төмендеді. For steamed bread made from frozen dough without adding HPMC, its cohesion was increased by O. 86-4-0.03 g (frozen storage 0 days) was reduced to 0.49+0.06 g (frozen storage for 60 days), while the restoring force was reduced from 0.48+0.04 g (frozen storage for 0 days) to 0.17±0.01 (frozen storage for 0 days) 60 days); however, for steamed buns made from frozen dough with 2% HPMC added, the cohesion was reduced from 0.93+0.02 g (0 days frozen) to 0.61+0.07 g (frozen storage for 60 days), while the restoring force was reduced from 0.53+0.01 g (frozen storage for 0 days) to 0.27+4-0.02 (frozen storage for 60 days). Сонымен қатар, мұздатылған сақтау уақытын ұзартумен бумен пісірілген нанның жабысқақ және саздыдығы айтарлықтай өсті. Бумен пісірілген нан үшін HPMC қоспай мұздатылған қамырдан жасалған, жабысқақ болу 336,54 + 37 артты. 24 (0 days of frozen storage) increased to 1232.86±67.67 (60 days of frozen storage), while chewiness increased from 325.76+34.64 (0 days of frozen storage) to 1005.83+83.95 (frozen for 60 days); however, for the steamed buns made from frozen dough with 2% HPMC added, the stickiness increased from 206.62+1 1.84 (frozen for 0 days) to 472.84. 96 + 45.58. Бұл HPMC қосу мұздатылған нанның құрылымының құрылымындағы өзгерістерді тиімді түрде тежейтінін көрсетеді. In addition, the changes in the texture properties of steamed bread caused by freezing storage (such as the increase of stickiness and chewiness and the decrease of recovery force) There is also a certain internal correlation with the change of steamed bread specific volume. Thus, dough properties (eg, farinality, elongation, and rheological properties) can be improved by adding HPMC to frozen dough, and HPMC inhibits the formation, growth, and redistribution of ice crystals (recrystallization process), making frozen dough The quality of the processed steamed buns is improved.
HydroxyPropyl метилеллюлозасы (HPMC) - гидрофильді коллоидты және оның қытай стиліндегі макаронмен (мысалы, бумен пісірілген нан), соңғы өнім әлі де жетіспейді. Зерттеудің негізгі мақсаты - HPMC жетілдірудің әсерін бағалау, HPMC-ді мұздатылған қамырдың әсерін және бумен пісірілген нанның сапасын зерттеу, сонымен қатар HPMC-ді бумен пісірілген нан мен басқа қытай стиліндегі ұн өнімдеріне қосуға арналған. Нәтижелер HPMC қамырдың алайық қасиеттерін жақсарта алатындығын көрсетеді. When the addition amount of HPMC is 2%, the water absorption rate of the dough increases from 58.10% in the control group to 60.60%; 2 минут 12,2 минутқа дейін өсті; Сонымен бірге, қамырдың пайда болу уақыты бақылау тобындағы 2,1 минуттан 1,5 диірменге дейін төмендеді; Әлсіздігі бақылау тобындағы 55 фудан 18 фуға дейін төмендеді. Сонымен қатар, HPMC сонымен қатар қамырдың созылу қасиеттерін жақсартты. HPMC мөлшерінің ұлғаюымен қамырдың ұзақтығы айтарлықтай өсті; едәуір қысқарды. Сонымен қатар, мұздатылған сақтау кезеңінде, HPMC қосу қамырдағы мұздатылатын судың мөлшерін қамырдың жоғарылауын азайтты, олар қамыр желісінің құрылымына, осылайша қамырды кристалданудан туындаған, қамырдың тұтастығының салыстырмалы тұрақтылығын және желінің тұтастығын қамтамасыз етеді, осылайша қамыр желісінің құрылымының тұрақтылығын арттырады. Соңғы өнімнің сапасына кепілдік беріледі.
Wheat gluten is the most abundant storage protein in wheat grains, accounting for more than 80% of the total protein. According to the solubility of its components, it can be roughly divided into glutenin (soluble in alkaline solution) and gliadin (soluble in alkaline solution). in ethanol solution). Among them, the molecular weight (mw) of glutenin is as high as 1x107Da, and it has two subunits, which can form intermolecular and intramolecular disulfide bonds; while the molecular weight of gliadin is only 1x104Da, and there is only one subunit, which can form molecules Internal disulfide bond [100]. Campos, Steffe, & Ng (1 996) divided the formation of dough into two processes: energy input (mixing process with dough) and protein association (formation of dough network structure). It is generally believed that during dough formation, glutenin determines the elasticity and structural strength of the dough, while gliadin determines the viscosity and fluidity of the dough [102]. Глютен протеинінің қамыр желісінің құрылымын қалыптастыруда ажырамас және ерекше рөлі бар және қамырды біріктіру, ViscoLasticity және су сіңірумен түсіретінін көруге болады.
Сонымен қатар, микроскопиялық тұрғыдан қамырдың үш өлшемді желілік құрылымын қалыптастыру молекулааралық және ішілік коваленттік облигациялардың (мысалы, диверсиялық облигациялар) және коваленттік емес облигациялар (мысалы, сутегі байланыстары, гидрогендік күштер) қалыптасуымен қатар жүреді [103]. Екінші байланыстың энергиясы болғанымен
Саны мен тұрақтылығы ковалентті байланыстан гөрі әлсіз, бірақ олар глютендің сәйкестігін сақтауда маңызды рөл атқарады [1041].
For frozen dough, under freezing conditions, the formation and growth of ice crystals (crystallization and recrystallization process) will cause the dough network structure to be physically squeezed, and its structural integrity will be destroyed, and microscopically. Accompanied by changes in the structure and properties of gluten protein [105'1061. As Zhao, et a1. . Сонымен қатар, глютен протеинінің кеңістіктік конформациялық өзгерістері және термодинамикалық қасиеттері қамырды өңдеу қасиеттері мен өнімнің сапасына әсер етеді. Therefore, in the process of freezing storage, it is of certain research significance to investigate the changes of water state (ice crystal state) and the structure and properties of gluten protein under different freezing storage time conditions.
Therefore, the purpose of this experiment is to use the wheat gluten dough (Gluten Dough) as the research model to investigate the content of HPMC (0, 0.5%) under different freezing storage time (0, 15, 30, 60 days) , 1%, 2%) on the state and distribution of water in the wet gluten system, gluten protein rheological properties, thermodynamic properties, and its physicochemical properties, and then explore the reasons for the Мұздатылған қамырдың өңдеу қасиеттерінің өзгеруі және байланысты проблемаларды түсінуді жақсарту үшін HPMC механизмінің проблемаларының рөлі.
Gluten anhui rui rui fu xiang fud co., ltd; Гидроксиппил метиллулозасы (жоғарыдағыдай) Aladdin Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.
3.2.2 тәжірибелік аппараттар
Ашу. R3 Rheometer
DSC. Q200 Дифференциалды сканерлеу калориметрі
722E спектрофотометрі
JSM. 6490LV вольфрам Сканерлеме сканерлеуші электронды микроскоп
HH сандық тұрақты температуралы су ваннасы
ME. 5 Ультра-микроэлектрондық баланс
NICOLET 67 Fourier Fourier инфрақызыл спектрометрі
ҚДС. Жоғары жылдамдықты тоңазытылған центрифуга 160 сағат
PB. Модель 10 PH өлшегіш
MX. S Edy eDy ағымдағы осцилляторды теріңіз
KJELTEC TM 8400 Автоматты KJeldahl азот анализаторы
Фабрикант
American TA компаниясы
American TA компаниясы
Шанхай Нумет компаниясы
Шанхай спектрі Құралдары Co., Ltd.
Термо Фишер, АҚШ
Anhui zhong ke zhong jia ғылыми құралдары CO., Ltd.
Термо Фишер, АҚШ
Германия Сертификат
Эксперименттерде қолданылатын барлық химиялық реагенттер аналитикалық сынып болды.
3.2.4 Эксперименталды әдіс
3.2.4.1 Глютеннің негізгі компоненттерін анықтау
Frequency sweep, the specific experimental parameters are set as follows - the strain is 0.5% (at LVR), and the frequency sweep range is 0.1 Hz. 10 Гц, ал басқа параметрлер кернеуді тазарту параметрлерімен бірдей. Scanning data is acquired in logarithmic mode, and 5 data points (plots) are recorded in the rheological curve for every 10-fold increase in frequency, so as to obtain the frequency as the abscissa, the storage modulus (G') and the loss modulus (G') is the rheological discrete curve of the ordinate. It is worth noting that after each time the sample is pressed by the clamp, the excess sample needs to be gently scraped with a blade, and a layer of paraffin oil is applied to the edge of the sample to prevent moisture during the experiment. of loss. Each sample was replicated three times.
Бот әдісі бойынша (2003) [2003 ж.) [1081, дифференциалды сканерлеу калориметрі (DSC.200) үлгілердің тиісті термодинамикалық қасиеттерін өлшеу үшін қолданылды.
Олардың ішінде үшеуі ылғалдың жасырын жылуын білдіреді, ал оның мәні - 334 J / г; MC дымқыл глютендің ылғалдылығын білдіреді (GB 50093.2010) бойынша өлшенеді (78]). Әр үлгі үш рет қайталанды.
(2) бидай глютенді ақуызының термиялық денатурация шыңының (TP) температурасын анықтау
Freeze-dry the frozen-storage-treated sample, grind it again, and pass it through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain gluten protein powder (this solid powder sample is also applicable to 2.8). 10 мг глютенді ақуыз үлгісі өлшеніп, алюминийден жасалған алюминийден жасалған (қатты үлгілер үшін). The DSC measurement parameters were set as follows, equilibrated at 20 °C for 5 min, and then increased to 100 °C at a rate of 5 °C/min, using nitrogen as the purge gas, and its flow rate was 80 mL/min. Using a sealed empty crucible as a reference, and use the analysis software Universal Analysis 2000 to analyze the obtained DSC curve to obtain the peak temperature of thermal denaturation of wheat gluten protein (Yes). Each sample is replicated three times.
Тегін сульфхидерлік топтардың мазмұны «Бверидг, Тома» және Накай әдісі бойынша анықталды, тиісті модификациялар. Судың салмағы 40 мг бидай протеинінің үлгісін салмаңыз, оны жақсылап шайқаңыз және оны 4 мл додекилдің диодексуалынан шығарыңыз
Sodium Sodium (SDS). Tris-hydroxymethyl aminomethane (Tris). Glycine (Gly). Tetraacetic acid 7, amine (EDTA) buffer (10.4% Tris, 6.9 g glycine and 1.2 g EDTA/L, pH 8.0, abbreviated as TGE, and then 2.5% SDS It was added to the above TGE solution (that is, prepared into SDS-TGE buffer), incubated at 25°C for 30 min, and shaken every 10 min. Then, the supernatant was obtained after centrifugation for 10 min at 4°C and 5000×g. First, the protein content in the supernatant was determined by the Coomassie brilliant blue (G.250) method. Then, to the supernatant was added O. 04 mL of Ellman's reagent (dissolve 5,5'. Dithio-2. Nitrobenzoic acid, DTNB at TGE to measure the solution, 4 RAG / ML), 25 ℃ су ваннасында 30 минуттан кейін, су ваннасында 412 NM абсорбациясын қосады, ал жоғарыдағы буфер бос бақылау ретінде пайдаланылды. Соңында, ақысыз күкіртпен қамтылған мазмұн келесі формула бойынша есептелді:
Among them, 73.53 is the extinction coefficient; A is the absorbance value; D is the dilution factor (1 here); G - ақуыз концентрациясы. Each sample was replicated three times.
According to Kontogiorgos, Goff, & Kasapis (2007) method [1111, 2 g of wet gluten mass was placed in a 10 mm diameter nuclear magnetic tube, sealed with plastic wrap, and then placed in a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus to measure the transverse relaxation time (n), the specific parameters are set as follows: 32 ℃ equilibrium for 3 min, the field strength is 0.43 T, the resonance frequency is 18.169 Hz, and the pulse sequence is Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG), and the pulse durations of 900 and 1 800 were set to 13¨s and 25¨s , respectively, and the pulse interval r was as small as possible to reduce the interference and diffusion of the decay curve. Бұл экспериментте ол 5 м-с-ға дейін қойылды. Each assay was scanned 8 times to increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), with a 1 s interval between each scan. The relaxation time is obtained from the following integral equation:
Using the CONTIN algorithm in the Provencher analysis software combined with the Laplace inverse transformation, the inversion is performed to obtain a continuous distribution curve. Әр үлгі үш рет қайталанды
3.2.4.7 Бидай глютенді ақуызының қайталама құрылымын анықтау
Use OMNIC software to perform automatic baseline correction and advanced ATR correction on the obtained full wavenumber infrared spectrum, and then use Peak. Fit 4.12 software performs baseline correction, Fourier deconvolution and second derivative fitting on the amide III band (1350 cm-1.1200 cm'1) until the fitted correlation coefficient (∥) reaches 0. 99 or more, the integrated peak area corresponding to the secondary structure of each protein is finally obtained, and the relative content of each secondary structure is calculated. Сомасы (%), яғни, ең жоғары аймақ / жалпы шыңы. Әр үлгі үшін үш параллель жасалды.
3.2.4.8 Глютен протеинінің беткі гидрофобты анықтау
3.2.4.9 Электронды микроскопты бақылау
All results are expressed as mean 4-standard deviation, and the above experiments were repeated at least three times except for scanning electron microscopy. Диаграммаларды сызу үшін 8.0 тауарын пайдаланыңыз және SPSS 19.0 үшін пайдаланыңыз. Дисперсия мен Дунканның бірнеше ауқымын тексеру әдісі, маңыздылық деңгейі 0,05 құрады.
3. Нәтижелер мен талқылау
3.3.1 HPMC қосымшасының әсері және дымқыл глютен массасының реологиялық қасиеттеріне дейін сақтау уақытының салдары
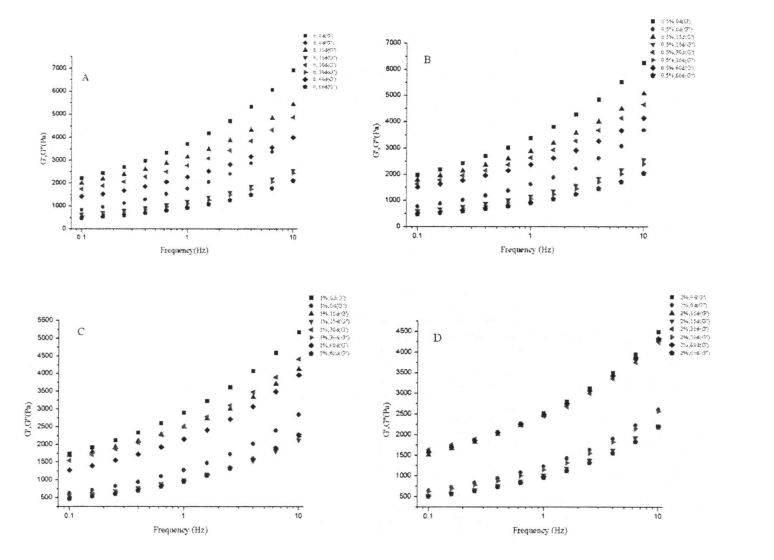
Rheological properties are an effective way to reflect the structure and properties of food materials and to predict and evaluate product quality [113J. Барлығымыздай, глютен протеині - бұл қамырды қамтуға мүмкіндік беретін негізгі материалдық компонент. 3.1-суретте көрсетілгендей, динамикалық жиілікті сыпыру (0,1.10 Гц) Нәтижелер (0.1.10 Гц) сулы глютенді бұқаралық үлгілердің (тұтқыр модуль, g ') жоғалту модулінен (g') (3.1-сурет, жарнамалық), бұл нәтиже, бұл нәтиже - бұл нәтиже The mutual cross-linking structure formed by covalent or non-covalent interaction is the backbone of the dough network structure [114]. At the same time, Sin Qu & Singh (2013) also believed that the rheological properties of dough are related to their protein components [114]. 115]. In addition, with the prolongation of freezing time, the G' and G' moduli of wet gluten doughs with 0%, 0.5% and 1% HPMC added showed different degrees of decrease (Fig. 3.1, 115). AC), and the degree of decrease was negatively correlated with the addition of HPMC, so that the G and G" moduli of wet gluten doughs with 2% HPMC addition did not show a significant increase with the freezing storage time from 0 to 60 days. Жыныстық айырмашылықтар (3.1, D сурет). This indicates that the three-dimensional network structure of the wet gluten mass without HPMC was destroyed by the ice crystals formed during the freezing process, which is consistent with the results found by Kontogiorgos, Goff, & Kasapis (2008), who believed that the prolonged freezing time caused the functionality and stability of the dough structure were seriously reduced.
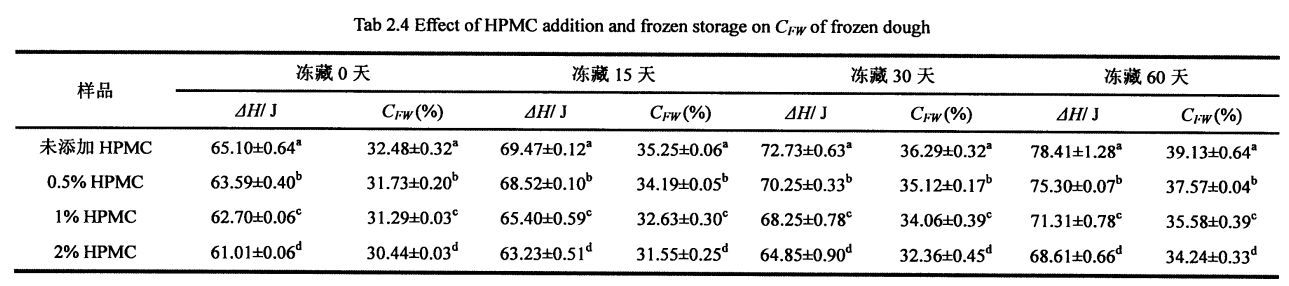
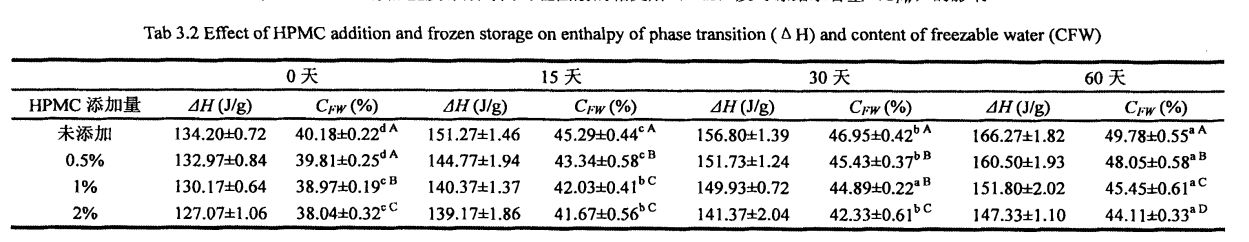
Ice crystals are formed by the phase transition of freezable water at temperatures below its freezing point. Therefore, the content of freezable water directly affects the number, size and distribution of ice crystals in the frozen dough. The experimental results (Table 3.2) show that as the freezing storage time is extended from 0 days to 60 days, the wet gluten mass Chinese silicon gradually becomes larger, which is consistent with the research results of others [117'11 81]. In particular, after 60 days of frozen storage, the phase transition enthalpy (day) of the wet gluten mass without HPMC increased from 134.20 J/g (0 d) to 166.27 J/g (60 d), that is, the increase increased by 23.90%, while the freezable moisture content (CF silicon) increased from 40.08% to 49.78%, an increase of 19.59%. Алайда, 0,5%, 1%, 1% және 2% ГЭС-мен толықтырылды, 6 күндік мұздатудан кейін, C-чат 20,07%, 16,0%, 16,0%, және 15,96%, бұл матураға сәйкес келеді, сонымен қатар A1. (2008) found that the melting enthalpy (Y) of the samples with added hydrophilic colloids decreased compared with the blank samples [119].
The increase in CFW is mainly due to the recrystallization process and the change of the gluten protein conformation, which changes the state of water from non-freezable water to freezable water. Ылғал күйіндегі бұл өзгерістер мұз кристалдарына желі құрылымының интерстазаларына түсуге мүмкіндік береді, желінің құрылымы біртіндеп (тері тесігі) біртіндеп үлкен болады, бұл біртіндеп тері тесігінің қабырғаларын қатты қысуға және жоюға әкеледі. However, the significant difference of 0w between the sample with a certain content of HPMC and the blank sample shows that HPMC can keep the water state relatively stable during the freezing process, thereby reducing the damage of ice crystals to the gluten network structure, and even inhibiting the quality of the product. нашарлау.
Глютеннің жылу тұрақтылығы астық қалыптастыруға және термиялық өңделген макарон өнімдерінің сапасына маңызды әсер етеді [211]. 3.2-сурет. Түзетуші DSC қисығы (° C), абсцисса және жылу ағыны (МВт) деп көрсетілген. The experimental results (Table 3.3) found that the heat denaturation temperature of gluten protein without freezing and without adding I-IPMC was 52.95 °C, which was consistent with Leon, et a1. (2003) and Khatkar, Barak, & Mudgil (2013) reported very similar results [120m11. With the addition of 0% unfrozen, O. Compared with the heat denaturation temperature of gluten protein with 5%, 1% and 2% HPMC, the heat deformation temperature of gluten protein corresponding to 60 days increased by 7.40℃, 6.15℃, 5.02℃ and 4.58℃, respectively. Айқындаудың бірдей уақытының жағдайында, денатурацияның ең жоғары температурасының жоғарылауы (N) деңгейі HPMC қосымшасының жоғарылауымен бірізді азайды. Бұл жылау нәтижелерінің өзгеру ережесіне сәйкес келеді. In addition, for the unfrozen samples, as the amount of HPMC added increases, the N values decrease sequentially. This may be due to the intermolecular interactions between HPMC with molecular surface activity and gluten, such as the formation of covalent and non-covalent bonds [122J].
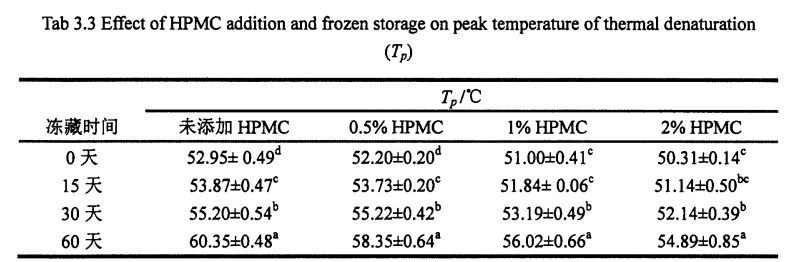
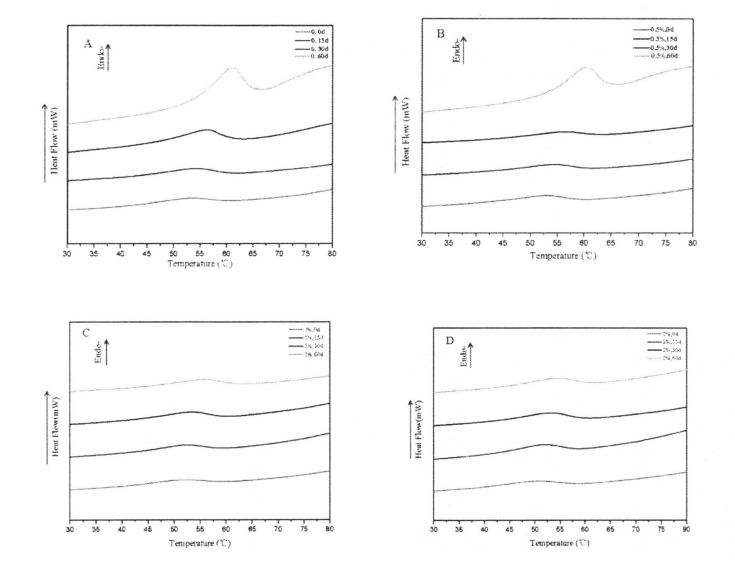
Fig 3.2 Typical DSC thermograms of gluten proteins with 0%HPMC(A);with O.5%HPMC(B); with 1%HPMC(C);with 2%HPMC(D)after different time of frozen storage,from 0d to 60d indicated from the lowest curve to the highest one in each graph. ЕСКЕРТПЕ: A - бұл HPMC қоспай бидай глютенінің DSC қисығы; B - бидай глютенінің 5% HPMC-мен DSC қисық сызығын қосу; C - бидай глютенінің DSC қисық сызығы, 1% HPMC; D - бидай глютенінің 2% глютені бар DSC-тің, HPMC-тің 2% грценінің қисық сызығы, HPMC қосымшасының әсері және сульффидрилдің құрамына еріту уақыты (C-SH) Коволекулалық коваленттік байланыстар, бұлт желінің құрылымының тұрақтылығы үшін өте маңызды. Диульфидті облигация (-SS-S-) - бұл екі тегін сульфондық топтардың дегидрогенциясы пайда болған ковалентті байланыс (.sh). Глутенин глутенин мен Глиадтан тұрады, ал екіншісі вентамолекулярлы және интермулярлы дисульфидті облигациялардан тұрады, ал соңғысы тек іштірткулярлы друльфидті облигацияларды қалыптастыра алады, сондықтан диульфидтік облигациялар - бұл интамелекулярлы / интермолекулалық емес диульсивті байланыс. Айналдырудың маңызды тәсілі. Compared to adding 0%, O. The C-SH of 5% and 1% HPMC without freezing treatment and the C-SH of gluten after 60 days of freezing have different degrees of increase respectively. Specifically, the face with no HPMC added gluten C. SH increased by 3.74 "mol/g to 8.25 "mol/g, while C.sh, shellfish, with gluten supplemented with 0.5% and 1% HPMC increased by 2.76 "mol/g to 7.25""mol/g and 1.33 "mol/g to 5.66 "mol/g (Fig. 3.3). Zhao, et a1. (2012) found that after 120 days of frozen storage, the content of free thiol groups increased significantly [ 1071. It is worth noting that the C-SH of gluten protein was significantly lower than that of other frozen storage periods when the freezing period was 15 days, which may be attributed to the freezing shrinkage effect of gluten protein structure, which makes the More intermolecular and intramolecular disulfide bonds were locally formed in a shorter freezing time [1161. Wang, et a1. (2014) found that the C-SH of glutenin-rich proteins was also significantly increased after 15 days of freezing. Decreased [1251. However, the gluten protein supplemented with 2% HPMC did not increase significantly except for C-SH, which also decreased significantly at 15 days, with the extension of freezing time.
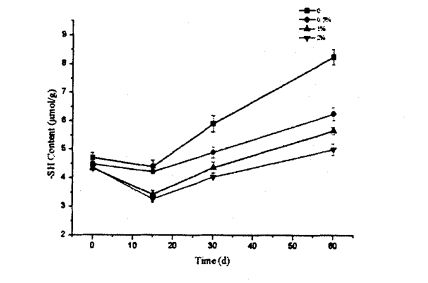
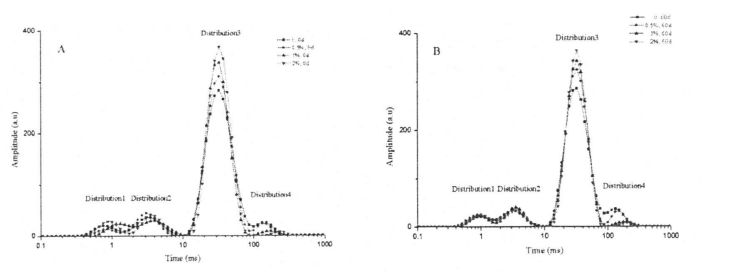
33 інжір 3,3-сурет. Жоғарыда айтылғандай, глютенді протеиндер үшін HPMC қосу және мұздатылған жадтың эффектісі жоғарыда айтылғандай, мұздатылатын су төмен температурада мұз кристалдарын қалыптастыра алады және глютен желісінің интерстазаларында таратуы мүмкін. Сондықтан, мұздату уақытын ұзартумен мұз кристалдары үлкенірек болады, бұл глютен протеинінің құрылымын байып, еркін және ішкі және ішкі экстрамолекулярлы дисульфидті облигациялардың сынуына әкеледі, бұл тегін күкіртсіз топтардың құрамын арттырады. Екінші жағынан, эксперименттік нәтижелер көрсеткендей, HPMC дифульфидті байланысын мұз кристалдарының экструзиялық зақымынан қорғауға, осылайша глютенді протеинді тежеуге болады. 3.3.4 HPMC қосымшасының әсері және пайдалану уақытының әсері Ылғал глютен массасының (T2) көлденең релаксация уақытында (T2) Көлденең релаксация уақытының (T2) таралуы азық-түлік материалдарындағы су көші-қонының модельін және динамикалық процесін көрсетуі мүмкін [6]. Figure 3.4 shows the distribution of wet gluten mass at 0 and 60 days with different HPMC additions, including 4 main distribution intervals, namely 0.1.1 ms (T21), 1.10 ms (T22), 10.100 ms (dead;) and 1 00-1 000 ms (T24). Босмандар және басқалар. (2012) found a similar distribution of wet gluten mass [1261], and they suggested that protons with relaxation times below 10 ms could be classified as rapidly relaxing protons, which are mainly derived from poor mobility the bound water, therefore, may characterize the relaxation time distribution of bound water bound to a small amount of starch, while Dang may characterize the relaxation time distribution of bound water bound to gluten protein. In addition, Kontogiorgos (2007) - t11¨, the "strands" of the gluten protein network structure are composed of several layers (Sheets) about 5 nm apart, and the water contained in these layers is limited water (or Bulk water, phase water), the mobility of this water is between the mobility of bound water and free water. Және T23-ті шектеулі судың релаксация уақытын таратуға жатқызуға болады. T24 таралуы (> 100 MS) ұзақ релаксацияға ие, сондықтан ол мықты ұтқырлықпен бос суды сипаттайды. Бұл су желінің құрылымында бар, ал глютенді ақуыз жүйесі бар әлсіз капиллярлық күш бар.
3.4 FRIPMC қосу және мұздатылған қойманың Ылғалы глютенді қамырға арналған көлденең релаксация уақыты
Comparing the wet gluten doughs with different addition amounts of HPMC stored in frozen storage for 60 days and unfrozen storage respectively, it was found that the total distribution area of T21 and T24 did not show a significant difference, indicating that the addition of HPMC did not significantly increase the relative amount of bound water. Мазмұн, ол негізгі су байланыстыратын заттардың (глютен протеині аз мөлшерде крахмалмен) грек сомасын қосу арқылы айтарлықтай өзгерген. On the other hand, by comparing the distribution areas of T21 and T24 of wet gluten mass with the same amount of HPMC added for different freezing storage times, there is also no significant difference, which indicates that the bound water is relatively stable during the freezing storage process, and has a negative impact on the environment. Changes are less sensitive and less affected.
Алайда, тоңазытылмаған және әр түрлі HPMC қоспалары бар және одан да әр түрлі HPMC қоспалары бар, сонымен қатар T23 таралуының биіктігі мен ауданы жоғарылағаны және қоспаның жоғарылауымен T23 биіктігі мен аймағындағы айқын айырмашылықтар болды (Cурет 3.4). This change shows that HPMC can significantly increase the relative content of limited water, and it is positively correlated with the added amount within a certain range. In addition, with the extension of freezing storage time, the height and area of T23 distribution of the wet gluten mass with the same HPMC content decreased to varying degrees. Therefore, compared with bound water, limited water showed a certain effect on freezing storage. Sensitivity. This trend suggests that the interaction between the gluten protein matrix and the confined water becomes weaker. Мұздату кезінде көбірек гидрофиялық топтар әсер етуі мүмкін, бұл термиялық денатурацияның температурасын өлшеуге сәйкес келеді. Атап айтқанда, 2% HPMC қосымшасы бар дымқыл глютендік массаға арналған T23 таралуының биіктігі мен ауданы айтарлықтай айырмашылықты көрсетпеді. Бұл HPMC судың көші-қонын және қайта бөлуге шектеліп, су күйін шектеулі күйден ауысуды тоқтату процесінде еркін күйге келтіруге кедергі келтіруі мүмкін.
Figure 3.5 is the infrared spectrum of the amide III band of gluten protein added with different contents of HPMC for 0 days after being frozen for 0 days after deconvolution and fitting of the second derivative. (2001) Екінші туынды шыңдарды бірдей шыңдармен безендірілген шыңдарға қолданды [1321]. In order to quantify the relative content changes of each secondary structure, Table 3.5 summarizes the relative percentage content of the four secondary structures of gluten protein with different freezing times and different HPMC additions (corresponding peak integral area/peak total area).
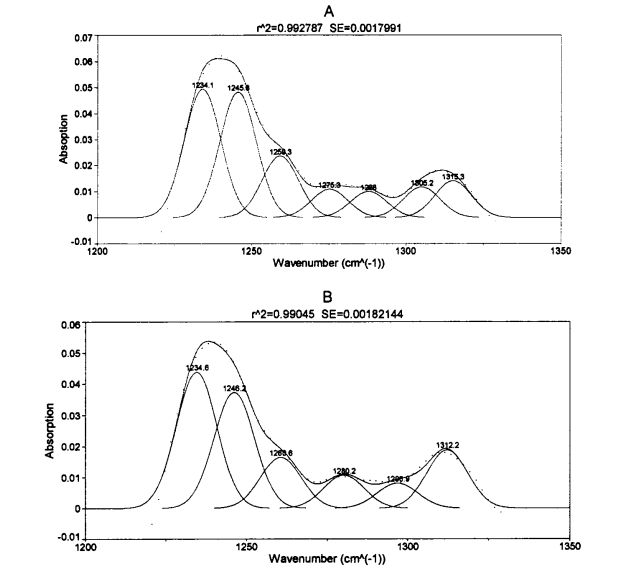
Ескерту: A бидай глютенді ақуызының инфрақызыл спектрі, мұздатылған сақтаудың 0 күніне HPMC қоспай; B is the infrared spectrum of wheat gluten protein of frozen storage for 0 days with 2% HPMC added
With the prolongation of frozen storage time, the secondary structure of gluten protein with different additions of HPMC changed to different degrees. Мұздатылған, сонымен қатар HPMC-тің екеуі де грцен протеинінің екінші құрылымына әсер ететінін көруге болады. Regardless of the amount of HPMC added, B. The folded structure is the most dominant structure, accounting for about 60%. Мұздатылған сақтаудан 60 күннен кейін 0%, 5% және 1% HPMC қосады, об глютені. The relative content of folds increased significantly by 3.66%, 1.87% and 1.16%, respectively, which was similar to the results determined by Meziani et al. (2011) [l33J]. However, there was no significant difference during frozen storage for gluten supplemented with 2% HPMC. In addition, when frozen for 0 days, with the increase of HPMC addition, p. The relative content of folds increased slightly, especially when the addition amount was 2%, p. The relative content of folds increased by 2.01%. D. The folded structure can be divided into intermolecular p. Бүктеу (ақуыз молекулаларының біріктіруімен туындаған), антипараллель б. Бүктелген және параллель б. Үш ішкі құрылым бүктелген және мұздату кезінде қандай ішкі құрылым пайда болатынын анықтау қиын
өзгерді. Some researchers believe that the increase in the relative content of the B-type structure will lead to an increase in the rigidity and hydrophobicity of the steric conformation [41], and other researchers believe that p. The increase in folded structure is due to part of the new β-Fold formation is accompanied by a weakening of the structural strength maintained by hydrogen bonding [421]. β- The increase in the folded structure indicates that the protein is polymerized through hydrophobic bonds, which is consistent with the results of the peak temperature of thermal denaturation measured by DSC and the distribution of transverse relaxation time measured by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Protein denaturation. On the other hand, added 0.5%, 1% and 2% HPMC gluten protein α-whirling. The relative content of helix increased by 0.95%, 4.42% and 2.03% respectively with the prolongation of freezing time, which is consistent with Wang, et a1. (2014) found similar results [134]. 0 of gluten without added HPMC. There was no significant change in the relative content of helix during the frozen storage process, but with the increase of the addition amount of freeze for 0 days. There were significant differences in the relative content of α-whirling structures.
3-сурет Гидрофобты гидротехникалық әсер of (A), суды қайта бөлу (B), және мұздатылған жұмыс уақытының ұлғайтуымен глютен матрицасындағы (C) 【31'138】
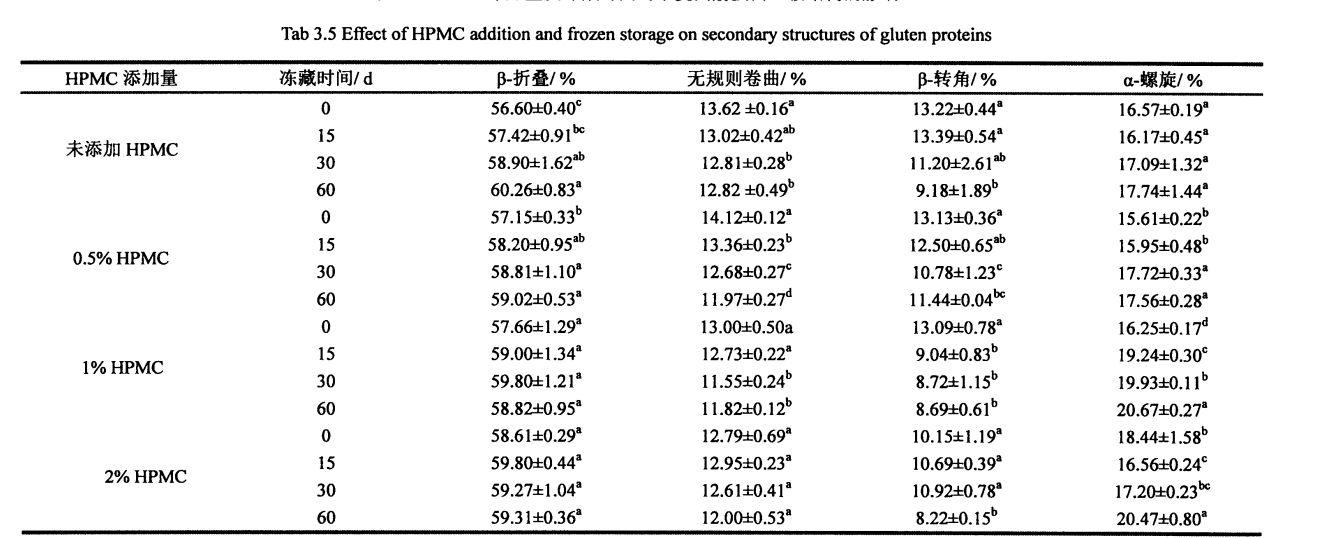
Мұздату уақытының ұзартқышы бар барлық үлгілер, б. The relative contents of the corners were significantly reduced. This shows that β-turn is very sensitive to freezing treatment [135. 1361], and whether HPMC is added or not has no effect. Wellner, et a1. (2005) proposed that the β-chain turn of gluten protein is related to the β-turn space domain structure of the glutenin polypeptide chain [l 37]. 2% HPMC-мен қосылған глютен протеинінің құрылымының салыстырмалы мазмұнын қоспағанда, мұздатылған қоймада айтарлықтай өзгерген жоқ, басқа үлгілер едәуір қысқарды, бұл мұз кристалдарының экструзиялануынан туындауы мүмкін. In addition, when frozen for 0 days, the relative contents of α-helix, β-sheet and β-turn structure of gluten protein added with 2% HPMC were significantly different from those of gluten protein without HPMC. This may indicate that there is an interaction between HPMC and gluten protein, forming new hydrogen bonds and then affecting the conformation of the protein; or HPMC absorbs the water in the pore cavity of the protein space structure, which deforms the protein and leads to more changes between the subunits. Жабу. The increase of the relative content of β-sheet structure and the decrease of the relative content of β-turn and α-helix structure are consistent with the above speculation. During the freezing process, the diffusion and migration of water and the formation of ice crystals destroy the hydrogen bonds that maintain the conformational stability and expose the hydrophobic groups of proteins. Сонымен қатар, энергия тұрғысынан, ақуыздың энергиясы аз, неғұрлым тұрақты болса, соғұрлым тұрақты. At low temperature, the self-organization behavior (folding and unfolding) of protein molecules proceeds spontaneously and leads to conformational changes.
Ақуыз молекулаларына гидрофильді және гидрофобты топтар кіреді. Generally, the protein surface is composed of hydrophilic groups, which can bind water through hydrogen bonding to form a hydration layer to prevent protein molecules from agglomerating and maintain their conformational stability. The interior of the protein contains more hydrophobic groups to form and maintain the secondary and tertiary structure of the protein through the hydrophobic force. Denaturation of proteins is often accompanied by exposure of hydrophobic groups and increased surface hydrophobicity.
TAB3.6 ГЭМК қосу және мұздатылған қойманың глютеннің гидрофобытте әсері

ЕСКЕРТПЕ: Бір қатарда м және В жоқ жол астындағы хат бар, бұл айтарлықтай айырмашылық бар екенін көрсетеді (<0,05);
60 күн мұздатылған қоймадан кейін 0%, o. Глютеннің беткі гидрофобтарының үстіне 5%, 1% және 2% HPMC 70,53%, тиісінше, 55,63%, 43,97% және 36,69% өсті (3.6-кесте). In particular, the surface hydrophobicity of the gluten protein without adding HPMC after being frozen for 30 days has increased significantly (P<0.05), and it is already greater than the surface of the gluten protein with 1% and 2% HPMC added after freezing for 60 days Hydrophobicity. At the same time, after 60 days of frozen storage, the surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein added with different contents showed significant differences. However, after 60 days of frozen storage, the surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein added with 2% HPMC only increased from 19.749 to 26.995, which was not significantly different from the surface hydrophobicity value after 30 days of frozen storage, and was always lower than other the value of the surface hydrophobicity of the sample. Бұл HPMC DCH-дің деформацияның ең жоғары температурасын анықтау нәтижелеріне сәйкес келетін глютенді ақуыздың денатурациясын тежеуі мүмкін екенін көрсетеді. This is because HPMC can inhibit the destruction of protein structure by recrystallization, and due to its hydrophilicity,
HPMC гидротехникалық топтардағы гидрофильді топтармен бірге екінші реттік облигациялар арқылы біріктіре алады, осылайша, гидрофобты топтардың әсерін шектеу кезінде ақуыздың беттік қасиеттерін өзгертеді (3.6-кесте).
3.3.7 HPMC қосымшасының әсері және глютеннің микро-желілік құрылымында сақтау уақытының әсері
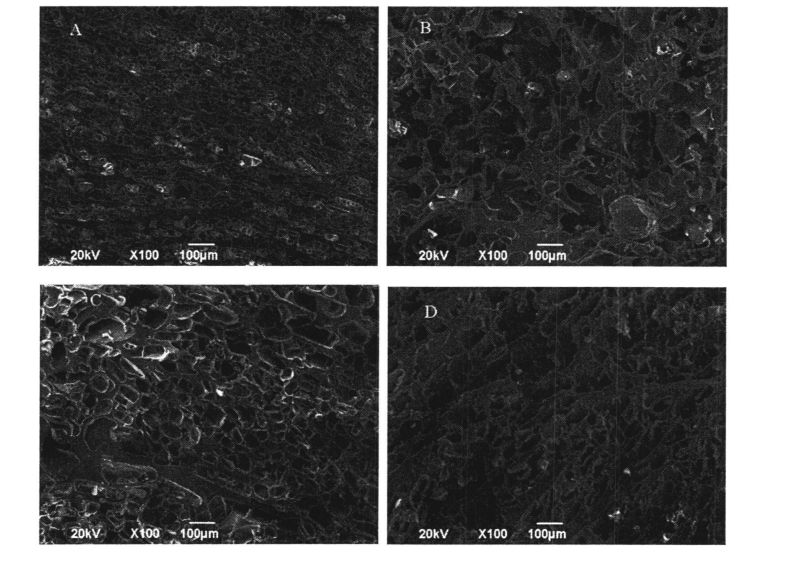
3,7-суретті глютен қамырының микроқұрылымы, (а) 0% мұздатылған сақтауға арналған 0% HPMC-мен глютенді қамыр; (с) 0% глютенді қамыр;
ЕСКЕРТПЕ: A GPMC қоспай және 0 күн ішінде мұздатылған глютен желісінің микроқұрылымы; B is the microstructure of gluten network without adding HPMC and frozen for 60 days; C is the microstructure of gluten network with 2% HPMC added and frozen for 0 days :D is the gluten network microstructure with 2% HPMC added and frozen for 60 days
60 күн мұздатылған қоймадан кейін HPMCсыз дымқыл глютендік массаның микроқұрылымы айтарлықтай өзгерді (Cурет 3.7, AB). At 0 days, the gluten microstructures with 2% or 0% HPMC showed complete shape, large
This experiment investigated the rheology of wet gluten dough and gluten protein by adding HPMC with different contents (0%, 0.5%, 1% and 2%) during freezing storage (0, 15, 30 and 60 days). Сипаттар, термодинамикалық қасиеттер, физика-химиялық қасиеттердің әсері. The study found that the change and redistribution of water state during the freezing storage process significantly increased the freezable water content in the wet gluten system, which led to the destruction of the gluten structure due to the formation and growth of ice crystals, and ultimately caused the processing properties of the dough to be different. Өнімнің сапасының нашарлауы. The results of frequency scanning showed that the elastic modulus and viscous modulus of the wet gluten mass without adding HPMC decreased significantly during the freezing storage process, and the scanning electron microscope showed that its microstructure was damaged. The content of free sulfhydryl group was significantly increased, and its hydrophobic group was more exposed, which made the thermal denaturation temperature and surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein significantly increased. However, the experimental results show that the addition of I-IPMC can effectively inhibit the changes in the structure and properties of wet gluten mass and gluten protein during freezing storage, and within a certain range, this inhibitory effect is positively correlated with the addition of HPMC. This is because HPMC can reduce the mobility of water and limit the increase of the freezable water content, thereby inhibiting the recrystallization phenomenon and keeping the gluten network structure and the spatial conformation of the protein relatively stable. Бұл HPMC қосу мұздатылған қамыр құрылымының тұтастығын тиімді сақтай алатындығын көрсетеді, осылайша өнімнің сапасын қамтамасыз етеді.
Starch is a chain polysaccharide with glucose as the monomer. key) two types. From a microscopic point of view, starch is usually granular, and the particle size of wheat starch is mainly distributed in two ranges of 2-10 pro (B starch) and 25-35 pm (A starch). From the perspective of crystal structure, starch granules include crystalline regions and amorphous regions (je, non-crystalline regions), and the crystal forms are further divided into A, B, and C types (it becomes V-type after complete gelatinization). Жалпы, кристалды аймақ амилопектиннен тұрады, ал аморфты аймақ негізінен амилозадан тұрады. This is because, in addition to the C chain (main chain), amylopectin also has side chains composed of B (Branch Chain) and C (Carbon Chain) chains, which makes amylopectin appear "tree-like" in raw starch. The shape of the crystallite bundle is arranged in a certain way to form a crystal.
Крахмал - ұнның негізгі компоненттерінің бірі, ал оның мазмұны шамамен 75% (құрғақ негіз). Сонымен бірге, астыққа көмірсулар сияқты, крахмал сонымен қатар тамақ өнімдеріндегі негізгі энергия көзі материалы болып табылады. Қамыр жүйесінде крахмал көбінесе глютенді ақуыздың желілік құрылымына қосылып, тіркелген. Өңдеу және сақтау кезінде крахмалар көбінесе желатинизация және қартаю кезеңдерінен өтеді.
Among them, starch gelatinization refers to the process in which starch granules are gradually disintegrated and hydrated in a system with high water content and under heating conditions. Ол шамамен үш негізгі процестерге бөлінуі мүмкін. 1) суды сіңіру сатысы; before reaching the initial temperature of gelatinization, the starch granules in the starch suspension (Slurry) keep their unique structure unchanged, and the external shape and internal structure basically do not change. Only very little soluble starch is dispersed in the water and can be restored to its original state. 2) су сіңірудің қайтымсыз кезеңі; as the temperature increases, water enters the gap between the starch crystallite bundles, irreversibly absorbs a large amount of water, causing the starch to swell, the volume expands several times, and the hydrogen bonds between the starch molecules are broken. It becomes stretched and the crystals disappear. At the same time, the birefringence phenomenon of starch, that is, the Maltese Cross observed under a polarizing microscope, begins to disappear, and the temperature at this time is called the initial gelatinization temperature of starch. 3) Starch granule disintegration stage; starch molecules completely enter the solution system to form starch paste (Paste/Starch Gel), at this time the viscosity of the system is the largest, and the birefringence phenomenon completely disappears, and the temperature at this time is called the complete starch gelatinization temperature, the gelatinized starch is also called α-starch [141]. When the dough is cooked, the gelatinization of starch endows the food with its unique texture, flavor, taste, color, and processing characteristics.
Көптеген зерттеулер көрсеткендей, Крахмал қоянының гель күші азаяды, ол жасқа жету оңай, сондықтан оның сапасы, мысалы, Тоғыз және А1 сияқты мұздату жағдайында оның сапасы нашарлайды. (2005) studied the effect of freezing temperature on the quality of potato starch puree; Ferrero, et a1. (1993) investigated the effects of freezing rate and different types of additives on the properties of wheat and corn starch pastes [151-156]. However, there are relatively few reports on the effect of frozen storage on the structure and properties of starch granules (native starch), which needs to be further explored. Мұздатылған қамыр (алдын ала пісірілген мұздатылған қамырды қоспағанда), мұздатылған сақтау жағдайындағы өзгермейтін түйіршіктер түрінде. Therefore, studying the structure and structural changes of native starch by adding HPMC has a certain effect on improving the processing properties of frozen dough. significance.
Wheat Starch Binzhou Zhongyu Food Co., Ltd.; HPMC Aladdin (Шанхай) химиялық реагент Co., Ltd;
HH сандық тұрақты температуралы су ваннасы
BSAL24S Электрондық тепе-теңдік
ҚДС. Жоғары жылдамдықты тоңазытылған центрифуга 160 сағат
С. 200 Дифференциалды сканерлеу калориметрі
D / max2500v типті x. ray ray Diffractometom
Фабрикант
Jiangsu Jintan Jincheng Guosheng Experatival Аспалды аспаптар фабрикасы
Shanghai Yiheng Service Cocial Co., Ltd.
Anhui zhongke zhonjjia sceet Cocial Co., Ltd.
American TA компаниясы
American TA компаниясы
4.2.3 Эксперименталды әдіс
1 г крахмал салмасы, 9 мл тазартылған су қосып, 10% (W / W) крахмалы суспензияны дайындау үшін толығымен шайқаңыз және араластырыңыз. Содан кейін үлгі шешімін қойыңыз. 18 ℃ Тоңазытқыш, мұздатылған қойма 0, 15 г, 30 г, 60 г, оның ішінде 0 күн - жаңа бақылау. Add 0.5%, 1%, 2% (w/w) HPMC instead of the corresponding quality starch to prepare samples with different addition amounts, and the rest of the treatment methods remain unchanged.
4.2.3.2 Реологиялық қасиеттері
(1) крахмал желатинизациясының сипаттамалары
Draw 1.5 mL of sample solution and add it to the center of the rheometer sample stage, measure the gelatinization properties of the sample according to the above program parameters, and obtain the time (min) as the abscissa, the viscosity (Pa s) and the temperature (°C) as the starch gelatinization curve of the ordinate. According to GB/T 14490.2008 [158], the corresponding gelatinization characteristic indicators—gelatinization peak viscosity (field), peak temperature (Ang), minimum viscosity (high), final viscosity (ratio) and decay value (Breakdown) are obtained. Қару, BV) және регенерация мәні (кері қайтару мәні, SV), онда ыдырау, ыдырау мәні = тұтқырлық - ең аз тұтқырлық; rubback мәні = түпкілікті тұтқырлық - минималды тұтқырлық. Әр үлгі үш рет қайталанды.
(2) крахмал пастасының тұрақты ағын сынағы
The above gelatinized starch paste was subjected to the Steady Flow Test, according to the method of Achayuthakan & Suphantharika [1591, the parameters were set to: Flow Sweep mode, stand at 25°C for 10 min, and the shear rate scan range was 1) 0.1 S one. 100S~, 2) 100s~. 0.1 S~, the data is collected in logarithmic mode, and 10 data points (plots) are recorded every 10 times the shear rate, and finally the shear rate (Shear Rate, SI) is taken as the abscissa, and the shear viscosity ( Viscosity, pa ·s) is the rheological curve of the ordinate. Тұтынудан шығу тегі 8.0 осы қисықтың сызықты еместігін және теңдеудің тиісті параметрлерін алуға, ал Қ., k сәйкес коэффициенті (PA-ген), яғни консистенция коэффициенті (1), ал n
4.2.3.3 Крахмалдан жасалған гельдік қасиеттері
2,5 г амилоидты алыңыз және оны тазартылған сумен 1: 2-ге араластырыңыз, крахмал сүтіне айналдыру. 18 ° C температурада 15 D, 30 D, және 60 г. Крахмалдың орнына 0,5, 1, 2% HPMC қосыңыз (W / W) және басқа дайындық әдістері өзгеріссіз қалады. Мұздату аяқталғаннан кейін, оны алыңыз, оны алыңыз, 4 ° C-тан 4 ° C-қа теңестіріп, сыналғанша бөлме температурасында ерітіп алыңыз.
Take 1.5 mL of sample solution and place it on the sample stage of the rheometer (Discovery.R3), press down the 40 m/n plate with a diameter of 1500 mm, and remove the excess sample solution, and continue to lower the plate to 1000 mm, on motor, the speed was set to 5 rad/s and rotated for 1 min to fully homogenize the sample solution and avoid the sedimentation of starch granules. Температураны сканерлеу 25 ° C-тан басталады және 5-те аяқталады. C / MIN 95 ° C-қа дейін өсті, 2 минут сақталады, содан кейін 5 «с / мин дейін 25 ° C дейін төмендетілді.
Петролатум қабаты келесі тәжірибелер кезінде судың жоғалуын болдырмау үшін жоғарыда алынған крахмал гельінің шетіне аздап жағылды. Referring to the Abebe & Ronda method [1601], an oscillatory strain sweep was firstly performed to determine the Linear Viscoelasticity Region (LVR), the strain sweep range was 0.01-100%, the frequency was 1 Hz, and the sweep was started after standing at 25 °C for 10 min.
After the corresponding freezing treatment time, the samples were taken out, thawed completely, and dried in an oven at 40 °C for 48 h. Finally, it was ground through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain a solid powder sample for use (suitable for XRD testing). Xie, және A1 қараңыз. (2014) method for sample preparation and determination of thermodynamic properties '1611, weigh 10 mg of starch sample into a liquid aluminum crucible with an ultra-micro analytical balance, add 20 mg of distilled water in a ratio of 1:2, press and seal it and place it at 4 °C In the refrigerator, equilibrated for 24 h. Freeze at 18°C (0, 15, 30 and 60 days). Add 0.5%, 1%, 2% (w/w) HPMC to replace the corresponding quality of starch, and other preparation methods remain unchanged. After the freezing storage time is over, take out the crucible and equilibrate at 4 °C for 4 h.
4.2.3.6 Крахмалдың ісіну қуатын анықтау
0,1 г кептірілген, жер және қабатты амилоидты 50 мл центрифуга түтігіне алыңыз, оған 10 мл тазартылған су қосыңыз, оны шайқаңыз, оны 0,5 сағат тұрыңыз, содан кейін оны 95 ° C-ты су ваннасына тұрақты температурада салыңыз. After 30 min, after gelatinization is complete, take out the centrifuge tube and place it in an ice bath for 10 min for rapid cooling. Соңында, 5000 айн / мин-ге центрифуга 20 минут және тұнба алу үшін супернатанды төгіп тастаңыз. Ісіну қуаты = Жауын-шашын масса / үлгі массасы [163].
4.2.3.7 Деректерді талдау және өңдеу
All experiments were repeated at least three times unless otherwise specified, and the experimental results were expressed as mean and standard deviation. SPSS статистикалық 19-сы 0,05 мәні бар дисперсияны талдауға (Anoviс, ANOVE) талдау үшін пайдаланылды; 4.0 көмегімен корреляциялық диаграммалар тартылды.
4.3 Талдау және талқылау
GB 50093.2010, GB / T 5009.9.2008, GB 50094.2010 (78-S0), бидай крахмалының негізгі компоненттері - ылғал, амилоза / амилопектин және күлдің негізгі компоненттері анықталды. The results are shown in Table 4. 1 shown.
4.1, бидай крахмалының құрамдас бөлігі
4.3.2 HPMC қосымшасының және мұздатылған сақтау уақытының эффектілері бидай крахмалының желатинизация сипаттамаларына әсер етуі
The starch suspension with a certain concentration is heated at a certain heating rate to make the starch gelatinized. Желдеткіштен басталғаннан кейін, Turbid сұйықтығы крахмалдың кеңеюіне байланысты біртіндеп паста болады, ал тұтқырлық үздіксіз артады. Subsequently, the starch granules rupture and the viscosity decreases. Паста белгілі бір салқындату жылдамдығында салқындатылған кезде, паста гель болады, ал тұтқырлық мәні одан әрі артады. The viscosity value when it is cooled to 50 °C is the final viscosity value (Figure 4.1).
With 1% HPMC) and 393.614-45.94 CP (with 2% HPMC), the retrogradation value decreased from 403.60+6.13 CP (without HPMC) to 427.29+14.50 CP, respectively (0.5% HPMC added), 360.484-41.39 CP (15 HPMC added) and 357.85+21.00 CP (2% HPMC қосылды). This and the addition of hydrocolloids such as xanthan gum and guar gum obtained by Achayuthakan & Suphantharika (2008) and Huang (2009) can increase the gelatinization viscosity of starch while reducing the retrogradation value of starch. This may be mainly because HPMC acts as a kind of hydrophilic colloid, and the addition of HPMC increases the gelatinization peak viscosity due to the hydrophilic group on its side chain which makes it more hydrophilic than starch granules at room temperature. In addition, the temperature range of the thermal gelatinization process (thermogelation process) of HPMC is larger than that of starch (results not shown), so that the addition of HPMC can effectively suppress the drastic decrease in viscosity due to the disintegration of starch granules. Сондықтан крахмал желатинизациясының минималды тұтқырлығы және түпкілікті тұтқырлығы HPMC мазмұнының артуымен біртіндеп өсті.
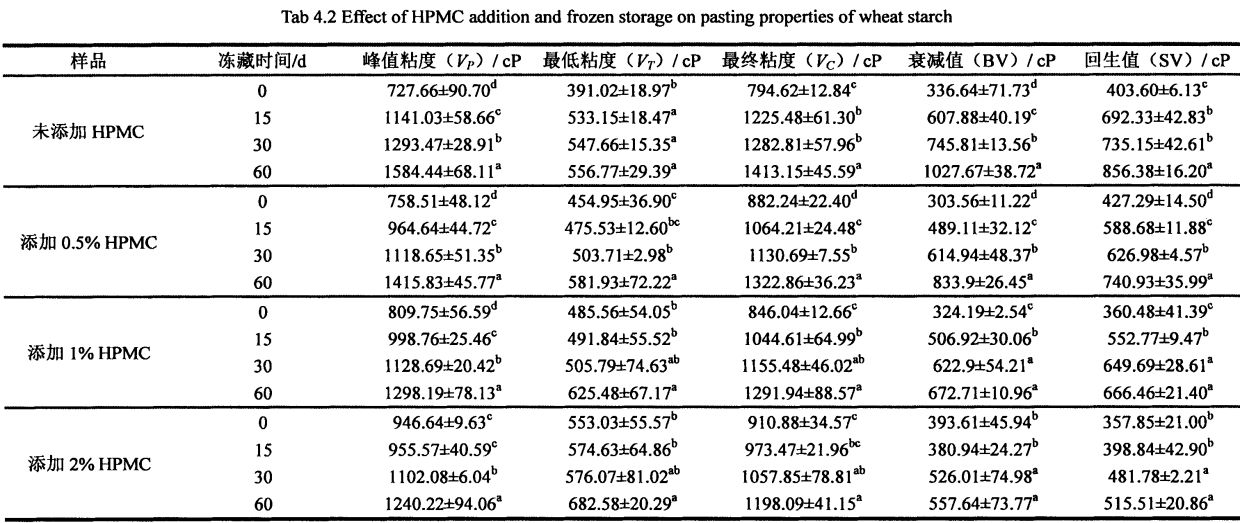
The final viscosity of starch suspension without adding HPMC increased from 794.62 ± 12.84 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1413.15 ± 45.59 CP (frozen storage for 60 days). The peak viscosity of starch suspension increased from 882.24 ± 22.40 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1322.86 ± 36.23 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); the peak viscosity of starch suspension added with 1% HPMC The viscosity increased from 846.04 ± 12.66 CP (frozen storage 0 days) to 1291.94 ± 88.57 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); және желатинизацияның жоғары деңгейі крахмал суспензиясының тұтқырлығы 2% HPMC-мен қосылды
(Мұздатылған қойма 0 күнге) 1198,09 ± 41.15 CP дейін (мұздатылған қойма) 60 күнге дейін өсті. Correspondingly, the attenuation value of starch suspension without adding HPMC increased from 336.64 ± 71.73 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1027.67 ± 38.72 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); 0,5 қосу% HPMC-мен крахмал суспензиясының құлдырау құндылығы 303,56 ± 11.22 СП (мұздатылған қойма) 833.9 ± 26.45 CP-ге дейін өсті (мұздатылған қойма); 60 күн ішінде); starch suspension with 1% HPMC added The attenuation value of the liquid was increased from 324.19 ± 2.54 CP (freezing for 0 days) to 672.71 ± 10.96 CP (freezing for 60 days); while adding 2% HPMC,the attenuation value of the starch suspension increased from 393.61 ± 45.94 CP (freezing for 0 days) to 557.64 ± 73.77 CP (freezing for 60 days); HPMCсыз крахмалды суспензиялау кезінде ретроградация мәні 403,60 ± 6.13 C-ге дейін өсті
Р (мұздатылған қойма 0 күнге арналған) 856,38 ± 16.20 CP дейін (60 күн бойы мұздатылған қойма); the retrogradation value of starch suspension added with 0.5% HPMC increased from 427 .29±14.50 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 740.93±35.99 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); the retrogradation value of starch suspension added with 1% HPMC increased from 360.48±41. 39 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 666.46 ± 21.40 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); while the retrogradation value of starch suspension added with 2% HPMC increased from 357.85 ± 21.00 CP (frozen storage for 60 days). 0 days) increased to 515.51 ± 20.86 CP (60 days frozen).
It can be seen that with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the starch gelatinization characteristics index increased, which is consistent with Tao et a1. f2015) 1. Consistent with the experimental results, they found that with the increase of the number of freeze-thaw cycles, the peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value, and retrogradation value of starch gelatinization all increased to different degrees [166J]. This is mainly because in the process of freezing storage, the amorphous region (Amorphous Region) of starch granules is destroyed by ice crystallization, so that the amylose (the main component) in the amorphous region (non-crystalline region) undergoes phase separation (Phase. separated) phenomenon, and dispersed in the starch suspension, resulting in an increase in the viscosity of starch gelatinization, және кері қайту құндылығының және ретроградация құнының ұлғаюы. However, the addition of HPMC inhibited the effect of ice crystallization on starch structure. Therefore, the peak viscosity, minimum viscosity, final viscosity, decay value and retrogradation rate of starch gelatinization increased with the addition of HPMC during frozen storage. increase and decrease sequentially.
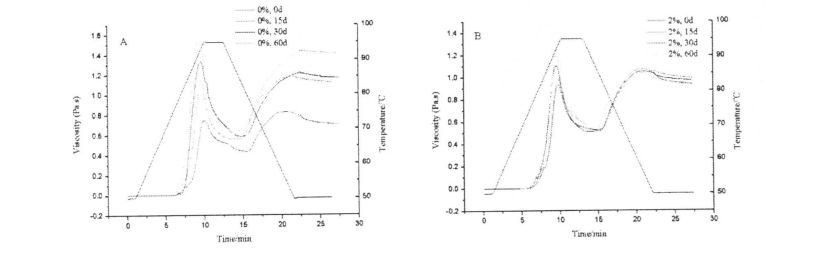
41-сурет, бидай крахмалы HPMC (A) немесе 2% HPMC①)
Сұйықтық тұтқырлығы бойынша ығысу деңгейінің әсері (сұйықтықтың тұтқырлығы) әсері тұрақты ағындармен зерттелді, ал сұйықтықтың материалдық құрылымы мен қасиеттері сәйкесінше көрініс тапты. Table 4.3 lists the equation parameters obtained by nonlinear fitting, that is, the consistency coefficient K and the flow characteristic index D, as well as the influence of the addition amount of HPMC and the freezing storage time on the above parameters K gate.
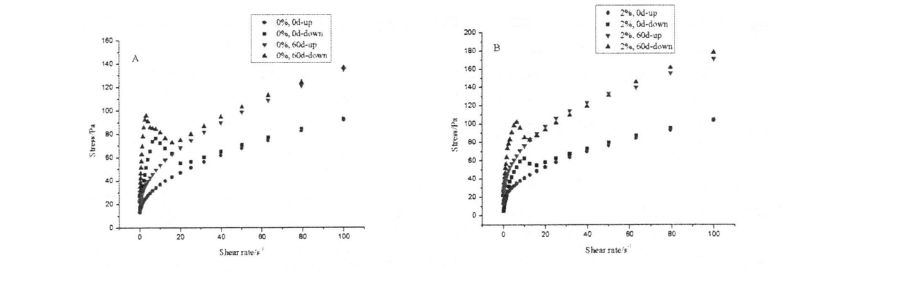
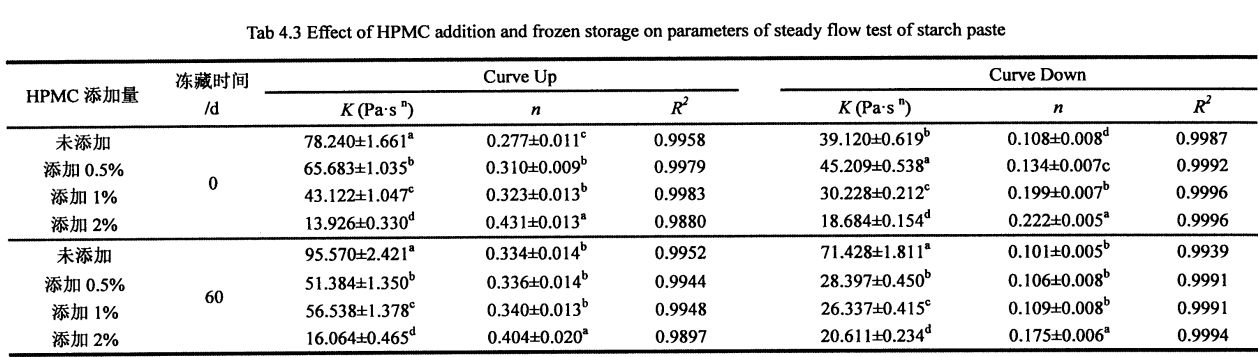
It can be seen from Table 4.3 that all the flow characteristic indices, 2, are less than 1. Therefore, starch paste (whether HPMC is added or whether it is frozen or not) belongs to Pseudoplastic Fluid, and all show shearing Thinning phenomenon (as the shear rate increases, the shear viscosity of the fluid decreases). In addition, the shear rate scans ranged from 0.1 s, respectively. 1 increased to 100 s ~, and then decreased from 100 sd to O. The rheological curves obtained at 1 sd do not completely overlap, and the fitting results of K, s are also different, so the starch paste is a thixotropic pseudoplastic fluid (whether HPMC is added or whether it is frozen or not). However, under the same freezing storage time, with the increase of HPMC addition, the difference between the fitting results of the K n values of the two scans gradually decreased, which indicates that the addition of HPMC makes the structure of starch paste under shear stress. Бұл іс-әрекеттің астында салыстырмалы түрде тұрақты болып қалады және «тиксотропты сақинаны» азайтады
(Thixotropic Циклі) аймағы, бұл Temsiripong және A1. (2005) reported the same conclusion [167]. This may be mainly because HPMC can form intermolecular cross-links with gelatinized starch chains (mainly amylose chains), which "bound" the separation of amylose and amylopectin under the action of shearing force. , құрылымның салыстырмалы тұрақтылығы мен біркелкілігін сақтау үшін (4.2-сурет, ығысу деңгейі бар қисық сызық, ал қастық және ығысуды күшейту).
Алайда, мұздатуды сақтау уақытының ұзартылуы, k және n мәндері әр түрлі дәрежеге дейін өсті, олардың ішінде k мәні 78,240 ± 1.661 Па-1-ден 1,661 Па-1-ге дейін (бұрылмаған, 0 күн) дейін 95,570 ± 1-ге дейін өсті. 2.421 Па · №10 күн), 65,683 ± 1,035 бабадан 65,683 ± 1,035-тен (5% HPMC, 0 күн) 51.384 ± 1,350-ге дейін (0,5%, HPMC, 60 күн), 43.122 ± 1.047 бакадан өсті (1% HPMC, 0 күн) 56.538 ± 1,378 Па · 1% HPMC, 60 күн))) 13.926 ± 0.330-дан 0,330-дан 0,330-ға дейін өсті (2% HPMC, 0 күн) 16.064 ± 0.465 Паханға дейін (2% HPMC, 60 күн); 0.277 ± 0.011 (without adding HPMC, 0 days) rose to O. 334±0.014 (no addition, 60 days), increased from 0.310±0.009 (0.5% HPMC added, 0 day) to 0.336±0.014 (0.5% HPMC added, 60 days), from 0.323 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 0 days) to 0.340 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 60 days), and from 0.431 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 60 days) 2% HPMC, 0 days) to 0.404+0.020 (add 2% HPMC, 60 days). By comparison, it can be found that with the increase of the addition amount of HPMC, the change rate of K and Knife value decreases successively, which shows that the addition of HPMC can make the starch paste stable under the action of shearing force, which is consistent with the measurement results of starch gelatinization characteristics. дәйекті.
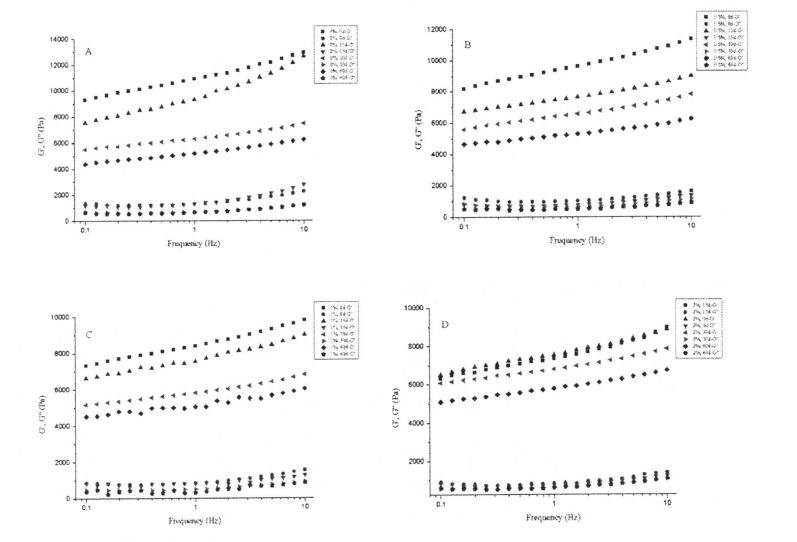
Note: A is the change of viscoelasticity of unadded HPMC starch with the extension of freezing storage time; B - бұл O. 5% HPMC крахмалының VisccaIlityLoy ext-тің аязды сақтау уақытын ұзартумен өзгеруі; C is the change of the viscoelasticity of 1% HPMC starch with the extension of freezing storage time; D is the change of the viscoelasticity of 2% HPMC starch with the extension of freezing storage time
The starch gelatinization process is accompanied by the disintegration of starch granules, the disappearance of the crystalline region, and the hydrogen bonding between starch chains and moisture, the starch gelatinized to form a heat-induced (Heat. induced) gel with a certain gel strength. As shown in Figure 4.3, for starch without frozen storage, with the increase of HPMC addition, the G' of starch decreased significantly, while G" had no significant difference, and tan 6 increased (Liquid. 1ike), which shows that during the gelatinization process, HPMC interacts with starch, and due to the water retention of HPMC, the addition of HPMC reduces the water loss of starch during the gelatinization process. At the same time, Chaisawang & Suphantharika (2005) found that, adding guar gum and xanthan gum to tapioca starch, the G' of the starch paste also decreased [170]. In addition, with the extension of the freezing storage time, the G' of starch gelatinized decreased to different degrees. This is mainly because during the frozen storage process of starch, the amylose in the amorphous region of starch granules is separated to form damaged starch (Damaged Starch), which reduces the degree of intermolecular cross-linking after starch gelatinization and the degree of cross-linking after cross-linking. Stability and compactness, and the physical extrusion of ice crystals makes the arrangement of "micelles" (microcrystalline structures, mainly composed of amylopectin) in the starch crystallization area more compact, increasing the relative crystallinity of starch, and at the same time , resulting in insufficient combination of molecular chain and water after starch gelatinization, low extension of molecular chain (molecular chain mobility), and Ақыры крахмалдың гельінің беріктігінен бас тартуға себеп болды. However, with the increase of HPMC addition, the decreasing trend of G' was suppressed, and this effect was positively correlated with the addition of HPMC. This indicated that the addition of HPMC could effectively inhibit the effect of ice crystals on the structure and properties of starch under frozen storage conditions.
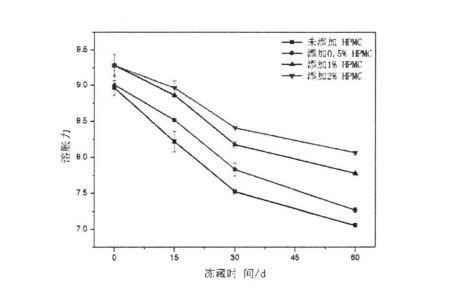
4.3.6 HPMC қосымшасының және мұздатылған сақтау уақытының эффектілері крахмалдың термодинамикалық қасиеттеріне
The gelatinization of starch is an endothermic chemical thermodynamic process. Therefore, DSC is often used to determine the onset temperature (Dead), peak temperature (To), end temperature (T p), and gelatinization enthalpy of starch gelatinization. (TC). 4.4-кестеде крахмал желатинизациясының DSC қисық сызықтары көрсетілген, олар 2%, және мұздату үшін әр түрлі уақыт ішінде HPMC қосылмаған.
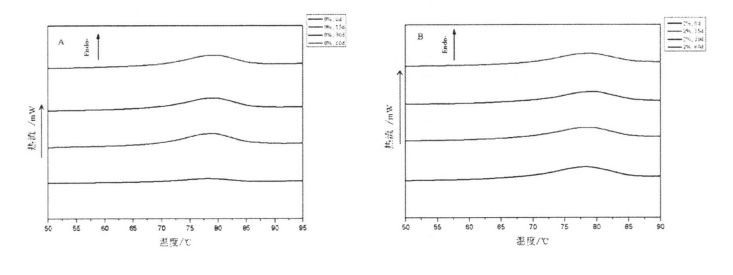
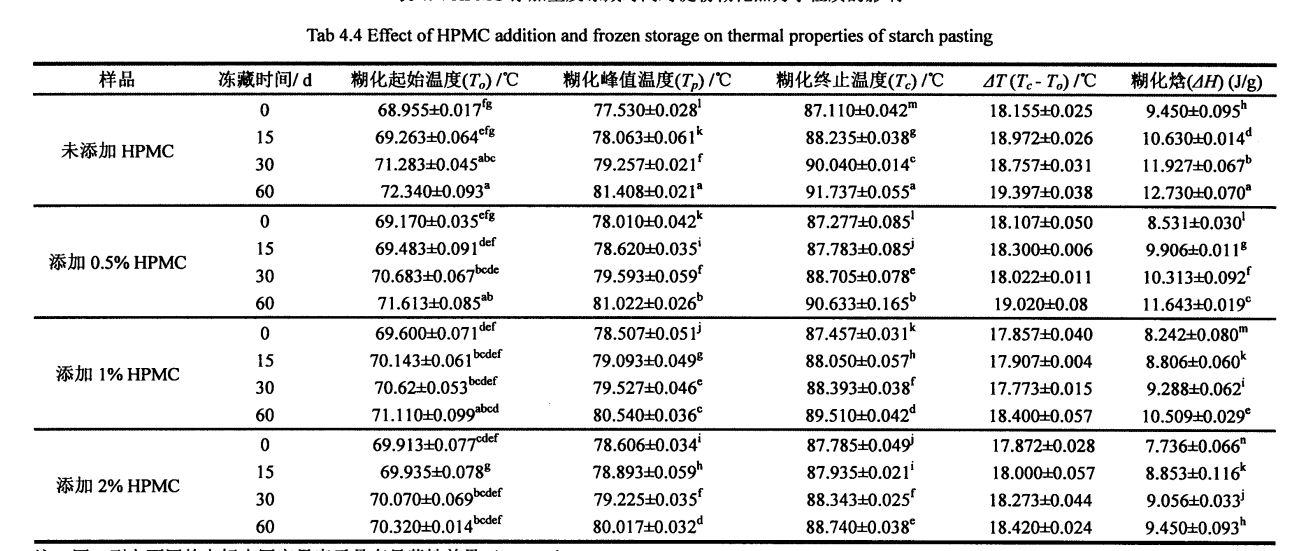
HPMC қосымшасының жоғарылауымен 4.4 кестеде көрсетілгендей, крахмалда едәуір айырмашылық жоқ, бірақ 77.530 ± 0.042-ге дейін (0,5% HPMC қосыңыз), 78.507 ± 0.041 (1% HPMC қосыңыз), және 78.606 ± 0.034 (2% қосыңыз) HPMC), бірақ 4H, бірақ 4H 9,450 ± 0.095-тен (HPMC қоспай) 8.53 ± 0.030-ға дейін (HPMC қоспай), 8.242a: 0.080 (1% HPMC) және 7 .736 ± 0.066 (2% HPMC қосыңыз). Бұл Чжоуға ұқсас, және A1. . This is mainly because HPMC has better hydrophilicity and is easier to combine with water than starch. At the same time, due to the large temperature range of the thermally accelerated gelation process of HPMC, the addition of HPMC increases the peak gelatinization temperature of starch, while the gelatinization Enthalpy decreases.
Екінші жағынан, крахмал желатинизациясы, t p, tc, tc, △ t және △ △ және △ залда мұздату уақытының ұзартылуымен артты. Specifically, starch gelatinization with 1% or 2% HPMC added had no significant difference after freezing for 60 days, while starch without or with 0.5% HPMC was added from 68.955±0.01 7 (frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 72.340 ± 0.093 (frozen storage for 60 days), and from 69.170 ± 0.035 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 71.613 ± 0.085 (frozen storage for 0 days) 60 days); after 60 days of frozen storage, the growth rate of starch gelatinization decreased with the increase of HPMC addition, such as starch without HPMC added from 77.530 ± 0.028 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 81.028. 408 ± 0.021 (frozen storage for 60 days), while the starch added with 2% HPMC increased from 78.606 ± 0.034 (frozen storage for 0 days) to 80.017 ± 0.032 (frozen storage for 60 days). days); in addition, ΔH also showed the same change rule, which increased from 9.450 ± 0.095 (no addition, 0 days) to 12.730 ± 0.070 (no addition, 60 days), respectively, from 8.450 ± 0.095 (no addition, 0 days) to 12.730 ± 0.070 (no addition, 60 days), respectively. 531 ± 0.030 (add 0.5%, 0 days) to 11.643 ± 0.019 (add 0.5%, 60 days), from 8.242 ± 0.080 (add 1%, 0 days) to 10.509 ± 0.029 (add 1%, 60 days), and from 7.736 ± O. 066 (2% addition, 0 days) rose to 9.450 ± 0.093 (2% addition, 60 days). The main reasons for the above-mentioned changes in the thermodynamic properties of starch gelatinization during the frozen storage process are the formation of damaged starch, which destroys the amorphous region (amorphous region) and increases the crystallinity of the crystalline region. The coexistence of the two increases the relative crystallinity of starch, which in turn leads to an increase in thermodynamic indexes such as starch gelatinization peak temperature and gelatinization enthalpy. Алайда, салыстыру арқылы, оны аязды сақтау уақытының астында, HPMC қосымшасының жоғарылауымен, крахмал желатинизациясының жоғарылауы, T P, T, TC, δt және δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ increaseн-ге дейін жоғарылауы бар екенін анықтауға болады. It can be seen that the addition of HPMC can effectively maintain the relative stability of the starch crystal structure, thereby inhibiting the increase of the thermodynamic properties of starch gelatinization.
4.3.7 I-IPMC қосудың әсері және крахмалдың салыстырмалы кристалдылығында ұстау уақытының әсері
X. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is obtained by X. X-ray diffraction is a research method that analyzes the diffraction spectrum to obtain information such as the composition of the material, the structure or morphology of the atoms or molecules in the material. Крахмал түйіршіктерінде крахмалы кристалды құрылымы бар, өйткені XRD крахмал кристалдарының кристаллографиялық формасы мен салыстырмалы кристалдылығын анықтау және анықтау үшін жиі қолданылады.
4.6-сурет. As shown in A, the positions of the starch crystallization peaks are located at 170, 180, 190 and 230, respectively, and there is no significant change in the peak positions regardless of whether they are treated by freezing or adding HPMC. Бұл бидай крахмалы кристалдануының ішкі қасиеті ретінде кристалды формасы тұрақты болып қалады.
However, with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the relative crystallinity of starch increased from 20.40 + 0.14 (without HPMC, 0 days) to 36.50 ± 0.42 (without HPMC, frozen storage, respectively). 60 күн), және 25.75 + 0,21-ден (2% HPMC қосылды, 0 күн) 32,70 ± 0,14 дейін (2% HPMC, 60 күн), осы және TAO және A1. (2016), the change rules of the measurement results are consistent [173-174]. The increase in relative crystallinity is mainly caused by the destruction of the amorphous region and the increase in the crystallinity of the crystalline region. In addition, consistent with the conclusion of the changes in the thermodynamic properties of starch gelatinization, the addition of HPMC reduced the degree of relative crystallinity increase, which indicated that during the freezing process, HPMC could effectively inhibit the structural damage of starch by ice crystals and maintain the Its structure and properties are relatively stable.
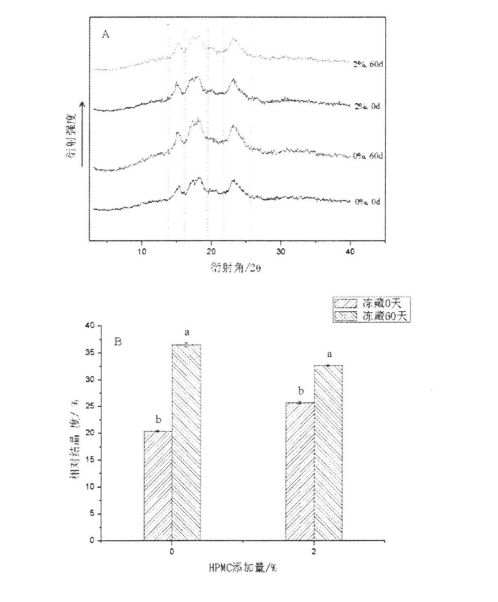
4-сурет, HPMC қосу және мұздатылған сақтаудың XRD қасиеттеріне әсері
Ескерту: a x. Рентгендік дифракцияның үлгісі; В - крахмалдың салыстырмалы кристалдық нәтижесі;
4.4 Тақырыптың қысқаша мазмұны
Крахмал - қамырдағы ең көп құрғақ зат, ол гелатинизациядан кейін, қамырдың өніміне бірегей қасиеттер (нақты көлем, құрылым, құрылым, сенсорлық, дәмді және т.б.) қосады. Since the change of starch structure will affect its gelatinization characteristics, which will also affect the quality of flour products, in this experiment, the gelatinization characteristics, flowability and flowability of starch after frozen storage were investigated by examining starch suspensions with different contents of HPMC added. Changes in rheological properties, thermodynamic properties and crystal structure were used to evaluate the protective effect of HPMC addition on starch granule structure and related properties. Эксперименттік нәтижелер бұған 60 күн мұздатылған қоймадан кейін, крахмалды желатинизацияның сипаттамалары (тұтқырлық, минималды тұтқырлық, минималды тұтқырлық, ыдыраудың минималды тұтқырлығы, ыдырау құндылығы және резервтік крест) салыстырмалы кресталықтың едәуір өсуіне және зақымдалған крахмалдың жоғарылауына байланысты. Гелатинизация энтальпия көбейді, ал крахмал пастасының гель күші айтарлықтай төмендеді; Алайда, әсіресе крахмал суспензиясы 2% HPMC-пен, салыстырмалы кристалдылығы және HPMC-дің зақымдану дәрежесі, сондықтан HPMC-тің қосылуы, желатинизация сипаттамаларына, желатинизацияның өзгеруіне және гельді қосқандағы гельді қосады, бұл HPMC қосымшасы крахмал құрылымы мен оның желатинизациясының қасиеттерін салыстырмалы түрде тұрақты етеді.
5.1 Кіріспе
Себебі HPMC суды сақтау және су ұстау қабілеті күшті, оны қамыр жүйесіне қосу мұз кристалдарының қалыптасуы мен өсуіне кедергі келтіруі мүмкін. In this experiment, different amounts of HPMC were added to the dough, and after a certain period of time after frozen storage, the quantity of yeast, fermentation activity and glutathione content in unit mass of dough were determined to evaluate the protective effect of HPMC on yeast under freezing conditions.
5.2 Материалдар мен әдістер
5.2.1 Тәжірибелік материалдар мен құралдар
Материалдар мен құралдар
BPS. 500CL constant temperature and humidity box
3M қатты кино колониясы тез есептеледі
ҚДС. Жоғары жылдамдықты тоңазытылған центрифуга 160 сағат
BDS. 200 Төңірлік биологиялық микроскоп
Фабрикант
Shanghai Yiheng Service Cocial Co., Ltd.
3-ші Америка Корпорациясы
Шанхай спектрі ғылыми құралдары Co., Ltd.
Anhui zhongke zhonjjia sceet Cocial Co., Ltd.
5.2.2 Эксперименталды әдіс
Weigh 3 g of active dry yeast, add it to a sterilized 50 mL centrifuge tube under aseptic conditions, and then add 27 mL of 9% (w/V) sterile saline to it, shake it up, and prepare 10% (w/w) yeast broth. Then, quickly move to. Store in a refrigerator at 18°C. After 15 d, 30 d, and 60 d of frozen storage, the samples were taken out for testing. Белсенді құрғақ ашытқы массасының сәйкес пайызын ауыстыру үшін 0,5%, 1%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2%, 2% қосыңыз. In particular, after the HPMC is weighed, it must be irradiated under an ultraviolet lamp for 30 minutes for sterilization and disinfection.
5.2.2.3 CFU (Colony-қалыптастыру қондырғылары) санау
Weigh 1 g of dough, add it to a test tube with 9 mL of sterile normal saline according to the requirements of the aseptic operation, shake it fully, record the concentration gradient as 101, and then dilute it into a series of concentration gradients until 10'1. Draw 1 mL of dilution from each of the above tubes, add it to the center of the 3M yeast rapid count test piece (with strain selectivity), and place the above test piece in a 25°C incubator according to the operating requirements and culture conditions specified by 3M. 5 D Мәдениет аяқталғаннан кейін алыңыз, алдымен морния морфологиясын байқаңыз, бұл оның ашытқының колония сипаттамаларына сәйкестігін, содан кейін санау және санауды санау үшін, содан кейін [179]. Each sample was repeated three times.
5.2.2.4 Глутатионның мазмұнын анықтау
The alloxan method was used to determine the glutathione content. The principle is that the reaction product of glutathione and alloxan has an absorption peak at 305 nl. Specific determination method: pipette 5 mL of yeast solution into a 10 mL centrifuge tube, then centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 min, take 1 mL of supernatant into a 10 mL centrifuge tube, add 1 mL of 0.1 mol/mL to the tube L alloxan solution, mixed thoroughly, then add 0.2 M PBS (pH 7.5) and 1 mL of 0.1 M, NaOH solution to it, Жақсылап араластырыңыз, бірден 6 мин, ал 1 м қосылыңыз, ал NaOH ерітінді 1 мл құрады, ал 305 нм-де сіңіру ультрафиолетпен араластырылған ультрафиолетпен араластырылған. Глутатион мазмұны стандартты қисықтан есептелді. Әр үлгі үш рет параллельді болды.
Experimental results are presented as 4-standard deviation of the mean, and each experiment was repeated at least three times. Analysis of variance was performed using SPSS, and the significance level was 0.05. Графиктерді сызу үшін пайда болуын қолданыңыз.

5-сурет. HPMC қосу және мұздатылған қойманың қамырды тексерудің биіктігіне әсері
5.1-суретте көрсетілгендей, 0 күн ішінде, HPMC мөлшерінің ұлғаюымен, қамырдың емделу биіктігі 4,234-0,11 см-ден 4,234-0,11 см-ге дейін, HPMC қоспай-ақ 4,234-0,1 см-ге дейін 4,234-0,1 см-ге дейін өсті. -0,12 см (HPMC қосылды), 4,314-0,19 см (қосылған HPMC) және 4,594-0,17 см (қосылған 2% HPMC). Алайда, 60 күн ішінде мұздатылғаннан кейін, қамырдың емтиленген биіктігі әртүрлі дәрежеде азайды. Атап айтқанда, қамырдың гпм-ді тексерудің биіктігі 4,234-0,11 см-ден (0 күнге тоңазыту) 3 .18 + 0,15 см-ге дейін азайтылды (тоңазытқыштар 60 күн ішінде мұздатылған қойма); 0,5% HPMC қосылған қамыр 4,27 + 0,12 см-ден (мұздатылған қойма) 3,424-0,22 см-ге дейін төмендеді (0 күнге дейін). 60 days); the dough added with 1% HPMC decreased from 4.314-0.19 cm (frozen storage for 0 days) to 3.774-0.12 cm (frozen storage for 60 days); 2% HPMC қосылған қамыр қосылған кезде оянды. The hair height was reduced from 4.594-0.17 cm (frozen storage for 0 days) to 4.09-±0.16 cm (frozen storage for 60 days). It can be seen that with the increase of the addition amount of HPMC, the degree of decrease in the proofing height of the dough gradually decreases. This shows that under the condition of frozen storage, HPMC can not only maintain the relative stability of the dough network structure, but also better protect the survival rate of yeast and its fermentation gas production activity, thereby reducing the quality deterioration of fermented noodles.
5.3.2 I-IPMC қосымшасының және аязды уақытты ашытқы өмір сүру деңгейіне әсер ету
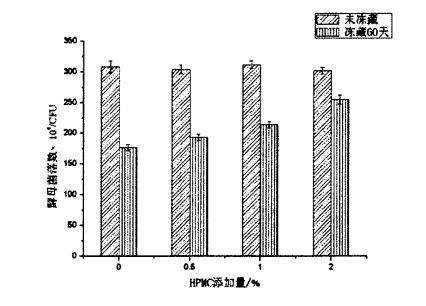
5.2-сурет, ашытқының өмір сүру деңгейі бойынша HPMC қосу және мұздатылған қойманың әсері
It can be seen from Figure 5.2 that there is no significant difference in the number of yeast colonies in samples with different contents of HPMC added without freezing treatment. This is similar to the result determined by Heitmann, Zannini, & Arendt (2015) [180]. However, after 60 days of freezing, the number of yeast colonies decreased significantly, from 3.08x106 CFU to 1.76x106 CFU (without adding HPMC); from 3.04x106 CFU to 193x106 CFU (adding 0.5% HPMC); reduced from 3.12x106 CFU to 2.14x106 CFU (added 1% HPMC); reduced from 3.02x106 CFU to 2.55x106 CFU (added 2% HPMC). Салыстыру арқылы мұздату ортасының күйзелісі ашытқы колониясының санының төмендеуіне әкеліп соқтыратын, бірақ HPMC қосымшасының жоғарылауымен, колония нөмірінің төмендеу дәрежесі төмендеді. Бұл HPMC ашытқыны мұздату жағдайында жақсы қорғайтындығын көрсетеді. Қорғау механизмі глицеринмен бірдей болуы мүмкін, негізінен, негізінен мұз кристалдарының қалыптасуы мен өсуіне кедергі келтіреді және төмен температуралық ортаға әсер етуді ашытқыңыз. 5.3-сурет - 3M ашытқысынан алынған фотомикрограф, ол 3M ашытқыларынан бастап, ашытқының сыртқы морфологиясына сәйкес келетін дайындық және микроскопиялық тексеруден кейін тез есептейді.
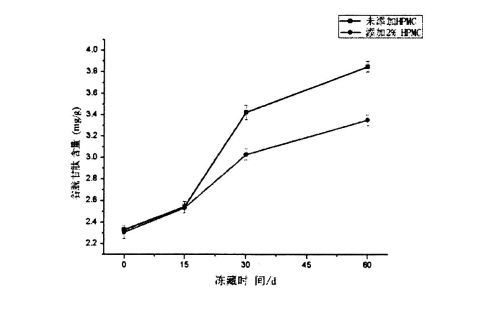
As shown in Figure 5.4, the glutathione content increased regardless of whether HPMC was added or not, and there was no significant difference between the different addition amounts. Бұл қамырды стресстің төзімділігі мен толеранттылығы нашарлататын кейбір белсенді құрғақ ашытқының кейбіреуі болуы мүмкін. Under the condition of low temperature freezing, the cells die, and then glutathione is released, which is only related to the characteristics of the yeast itself. Бұл сыртқы ортаға байланысты, бірақ қосылған HPMC мөлшеріне ешқандай қатысы жоқ. Сондықтан глутатионның мазмұны 15 күн ішінде өсіп, екеуінің арасында айтарлықтай айырмашылық болған жоқ. However, with the further extension of the freezing time, the increase of glutathione content decreased with the increase of HPMC addition, and the glutathione content of the bacterial solution without HPMC was increased from 2.329a: 0.040mg/ g (frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 3.8514-0.051 mg/g (frozen storage for 60 days); while the yeast liquid added 2% HPMC, its glutathione content increased from 2.307+0 .058 mg/g (frozen storage for 0 days) rose to 3.351+0.051 mg/g (frozen storage for 60 days). This further indicated that HPMC could better protect yeast cells and reduce the death of yeast, thereby reducing the content of glutathione released to the outside of the cell. This is mainly because HPMC can reduce the number of ice crystals, thereby effectively reducing the stress of ice crystals to yeast and inhibiting the increase of extracellular release of glutathione.
Yeast is an indispensable and important component in fermented flour products, and its fermentation activity will directly affect the quality of the final product. In this experiment, the protective effect of HPMC on yeast in frozen dough system was evaluated by studying the effect of different HPMC additions on yeast fermentation activity, yeast survival number, and extracellular glutathione content in frozen dough. Тәжірибелер арқылы HPMC қосу ашытқының ашыту белсенділігін жақсы ұстай алатындығы және 60 күндік мұздатудан кейін қамырдың әсер ету деңгейінің төмендеу дәрежесін азайтып, қорытынды өнімнің нақты көлеміне кепілдік береді; in addition, the addition of HPMC effectively The decrease of yeast survival number was inhibited and the increase rate of reduced glutathione content was reduced, thereby alleviating the damage of glutathione to dough network structure. This suggests that HPMC can protect yeast by inhibiting the formation and growth of ice crystals.
POST уақыты: қазан-08-2022